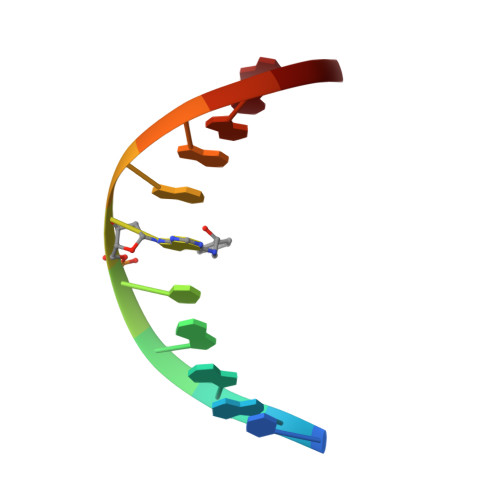
The nonmutagenic (R)- and (S)-beta-(N(6)-adenyl)styrene oxide adducts are oriented in the major groove and show little perturbation to DNA structure.
Hennard, C., Finneman, J., Harris, C.M., Harris, T.M., Stone, M.P.(2001) Biochemistry 40: 9780-9791
- PubMed: 11502171
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi010564v
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1K5E, 1K5F - PubMed Abstract:
Conformations of (R)-beta-(N(6)-adenyl)styrene oxide and (S)-beta-(N(6)-adenyl)styrene oxide adducts at position X(6) in d(CGGACXAGAAG).d(CTTCTTGTCCG), incorporating codons 60, 61 (underlined), and 62 of the human N-ras protooncogene, were refined from (1)H NMR data. These were designated as the beta-R(61,2) and beta-S(61,2) adducts. A total of 533 distance restraints and 162 dihedral restraints were used for the molecular dynamics calculations of the beta-S(61,2) adduct, while 518 distances and 163 dihedrals were used for the beta-R(61,2) adduct. The increased tether length of the beta-adducts results in two significant changes in adduct structure as compared to the corresponding alpha-styrenyl adducts [Stone, M. P., and Feng, B. (1996) Magn. Reson. Chem. 34, S105-S114]. First, it reduces the distortion introduced into the DNA duplex. For both the beta-R(61,2) and beta-S(61,2) adducts, the styrenyl moiety was positioned in the major groove of the duplex with little steric hindrance. Second, it mutes the influence of stereochemistry at the alpha-carbon such that both the beta-R(61,2) and beta-S(61,2) adducts exhibit similar conformations. The results were correlated with site-specific mutagenesis experiments that revealed the beta-R(61,2) and beta-S(61,2) adducts were not mutagenic and did not block polymerase bypass.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Center in Molecular Toxicology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee 37235, USA.