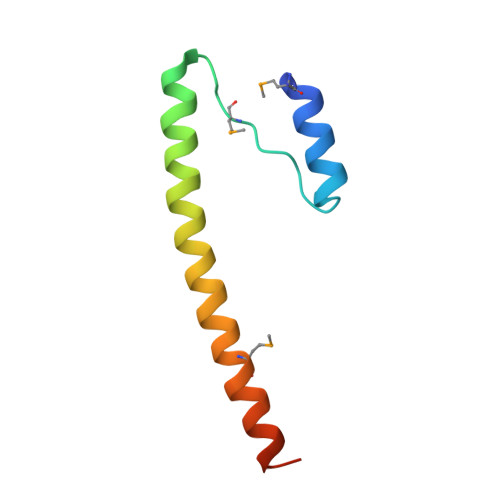
Structure of the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein oligomerization domain.
Zhao, X., Ghaffari, S., Lodish, H., Malashkevich, V.N., Kim, P.S.(2002) Nat Struct Biol 9: 117-120
- PubMed: 11780146
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb747
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1K1F - PubMed Abstract:
The Bcr-Abl oncoprotein is responsible for a wide range of human leukemias, including most cases of Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oligomerization of Bcr-Abl is essential for oncogenicity. We determined the crystal structure of the N-terminal oligomerization domain of Bcr-Abl (residues 1-72 or Bcr1-72) and found a novel mode of oligomer formation. Two N-shaped monomers dimerize by swapping N-terminal helices and by forming an antiparallel coiled coil between C-terminal helices. Two dimers then stack onto each other to form a tetramer. The Bcr1-72 structure provides a basis for the design of inhibitors of Bcr-Abl transforming activity by disrupting Bcr-Abl oligomerization.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Nine Cambridge Center, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142-1401, USA.