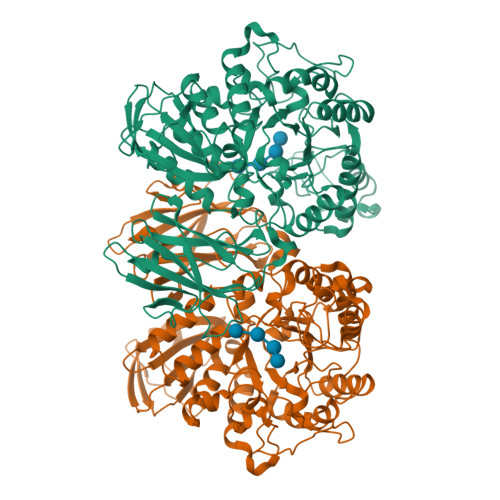
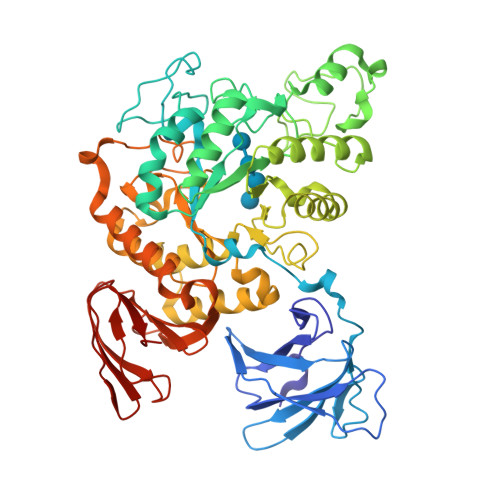
Structures of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 alpha-amylase II complexed with substrate analogues.
Yokota, T., Tonozuka, T., Shimura, Y., Ichikawa, K., Kamitori, S., Sakano, Y.(2001) Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65: 619-626
- PubMed: 11330677
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.65.619
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JIB, 1JL8 - PubMed Abstract:
The structures of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 alpha-amylase II mutant (d325nTVA II) complexed with substrate analogues, methyl beta-cyclodextrin (m beta-CD) and maltohexaose (G6), were solved by X-ray diffraction at 3.2 A and 3.3 A resolution, respectively. In d325nTVA II-m beta-CD complex, the orientation and binding-position of beta-CD in TVA II were identical to those in cyclodextin glucanotransferase (CGTase). The active site residues were essentialy conserved, while there are no residues corresponding to Tyr89, Phe183, and His233 of CGTase in TVA II. In d325nTVA II-G6 complex, the electron density maps of two glucosyl units at the non-reducing end were disordered and invisible. The four glucosyl units of G6 were bound to TVA II as in CGTase, while the others were not stacked and were probably flexible. The residues of TVA II corresponding to Tyr89, Lys232, and His233 of CGTase were completely lacking. These results suggest that the lack of the residues related to alpha-glucan and CD-stacking causes the functional distinctions between CGTase and TVA II.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Applied Biological Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Fuchu-shi, Japan.