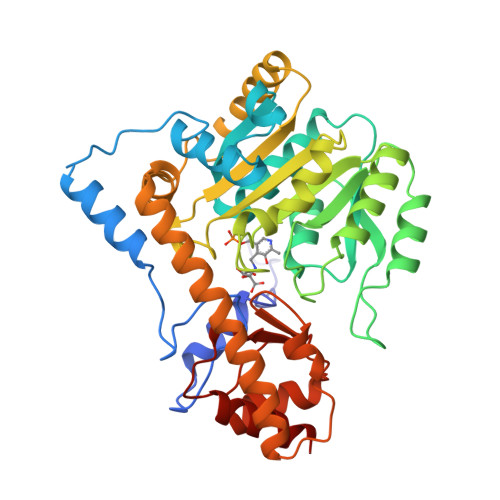
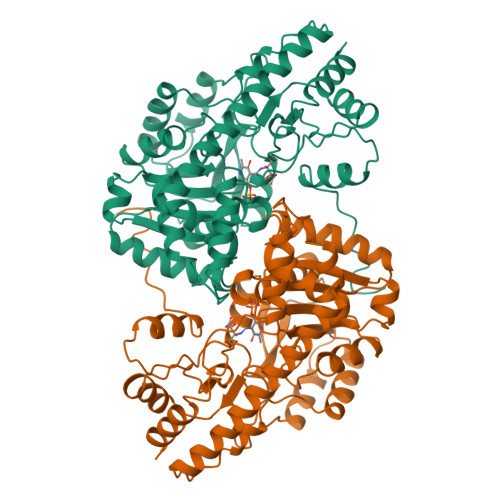
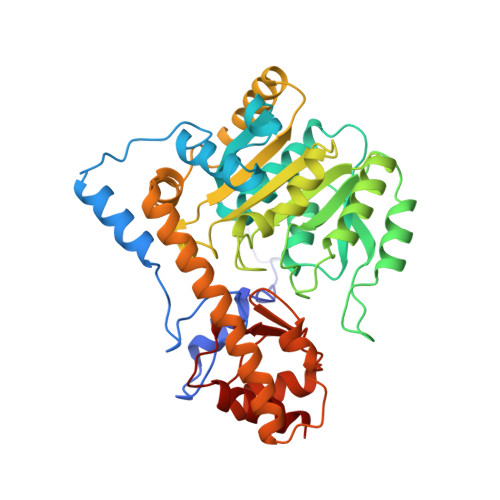
Aspartate aminotransferase complexed with erythro-beta-hydroxyaspartate: crystallographic and spectroscopic identification of the carbinolamine intermediate.
von Stosch, A.G.(1996) Biochemistry 35: 15260-15268
- PubMed: 8952476
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi960994z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IVR - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase (mAAT) of chicken complexed with erythro-beta-hydroxyaspartate has been determined at 2.4 A resolution. Pregrown crystals of mAAT complexed with the inhibitor maleate (closed enzyme conformation, orthorhombic space group C222(1)) were soaked in solutions of erythro-beta-hydroxyaspartate. The ligand exchange was monitored by microspectrophotometry. The active site turned out to be predominantly occupied by the carbinolamine intermediate. The carbinolamine is a true intermediate of the catalytic cycle forming the last covalently bound enzyme:substrate complex before release of the keto acid product. Occupancies of approximately 80% for the carbinolamine and of approximately 20% for the quinonoid intermediate were obtained. Two hydrogen bonds were identified that are potentially relevant for the accumulation of the carbinolamine intermediate: one to the hydroxyl group of Tyr 70* and the other to the epsilon-NH2 group of Lys 258.