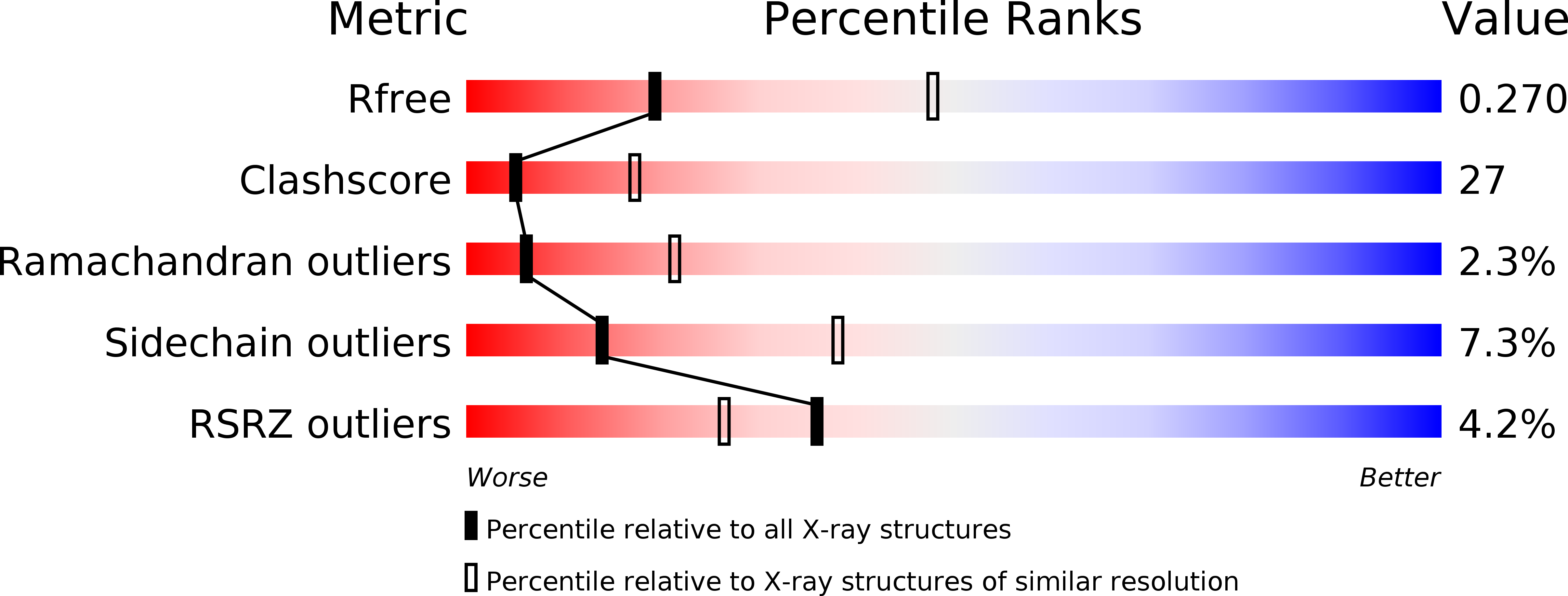
Atomic Structure of the Clamp Loader Small Subunit from Pyrococcus furiosus
Oyama, T., Ishino, Y., Cann, I.K.O., Ishino, S., Morikawa, K.(2001) Mol Cell 8: 455-463
- PubMed: 11545747
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00328-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IQP - PubMed Abstract:
In eukaryotic DNA replication, replication factor-C (RFC) acts as the clamp loader, which correctly installs the sliding clamp onto DNA strands at replication forks. The eukaryotic RFC is a complex consisting of one large and four small subunits. We have determined the crystal structure of the clamp loader small subunit (RFCS) from Pyrococcus furiosus. The six subunits, of which four bind ADP in their canonical nucleotide binding clefts, assemble into a dimer of semicircular trimers. The crescent-like architecture of each subunit formed by the three domains resembles that of the delta' subunit of the E. coli clamp loader. The trimeric architecture of archaeal RFCS, with its mobile N-terminal domains, involves intersubunit interactions that may be conserved in eukaryotic functional complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology and, Biomolecular Engineering Research Institute, 6-2-3 Furuedai, Suita-City, 565-0874, Osaka, Japan.