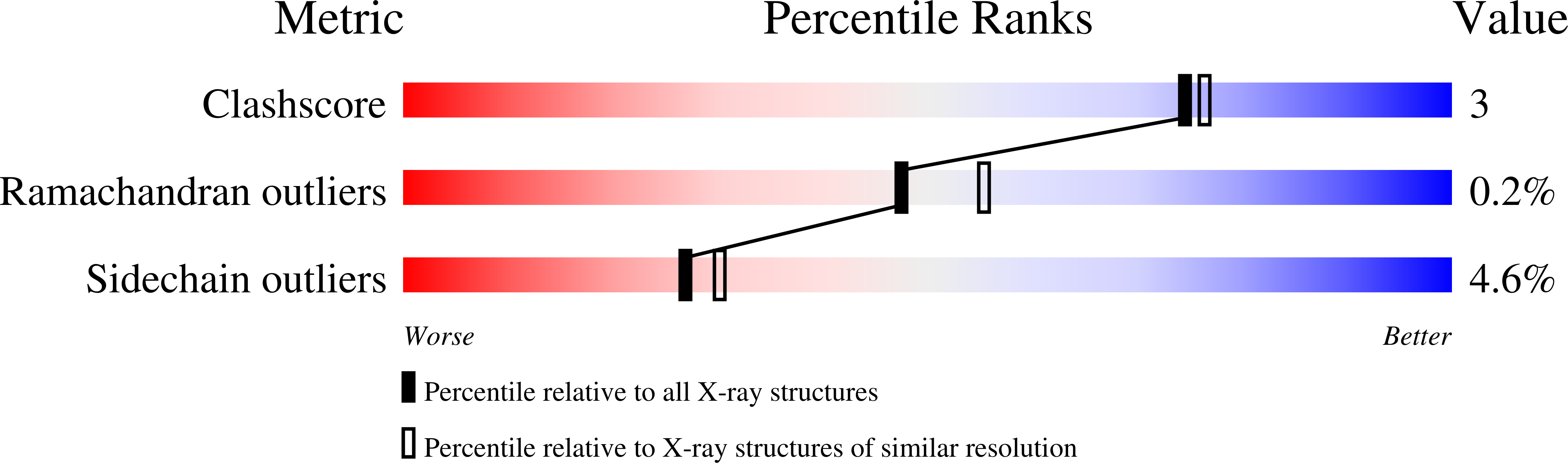Structural studies of metal binding by inositol monophosphatase: evidence for two-metal ion catalysis.
Bone, R., Frank, L., Springer, J.P., Atack, J.R.(1994) Biochemistry 33: 9468-9476
- PubMed: 8068621
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00198a012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IMC, 1IMD, 1IME, 1IMF - PubMed Abstract:
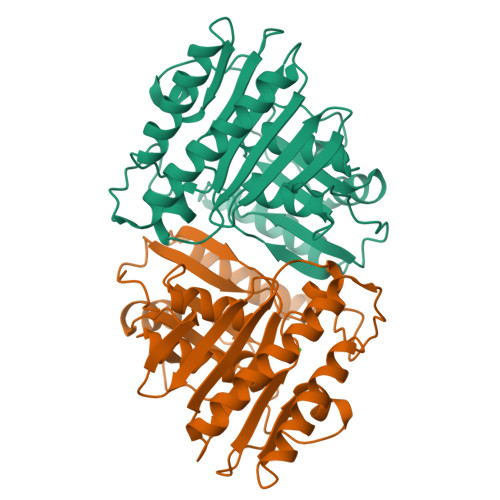
The structure of inositol monophosphatase has been determined to 2.60 A resolution in complexes with Mn2+ and with Mn2+ and phosphate. In the Mn2+ complex, three metal cations and one Cl were bound in the active site on each of the two subunits of the enzyme. Ligands to the three metals include the side chains of Glu 70, Asp 90, Asp 93, and Asp 220, t he carbonyl group of Ile 92, several solvent molecules and the chloride, which is a ligand to each of the cations. When phosphate is soaked into these Mn2+ cocrystals, one of the three Mn2+ ions is expelled from the active site, leaving metal ions with octahedral and tetrahedral coordination geometry. In addition, the structure of apoinositol monophosphatase was determined to 2.5 A resolution. Residues 70-75, a two-turn helical segment which is involved in metal coordination, moves away from the metal binding site by 2-3 A in the absence of cations. Residues 30-40, which wrap around the metal binding site and interact with the metal indirectly through solvent molecules and protein ligands to the metal, become disordered in the absence of metal. In various metal complexes, segmental mobility is also observed in the residues which form the metal binding sites. The results of these studies of the interaction of inositol monophosphatase with cations suggest that the enzyme accomplishes phosphate ester hydrolysis using two metal ions, one with octahedral and one with tetrahedral coordination geometry. Broad metal-binding specificity appears to result from extensive flexibility in several of the protein segments which contribute metal ligands, from the presence of alternate metal ligands and from metal coordination spheres which include water molecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysical Chemistry, Merck Research Laboratories, Rahway, New Jersey 07065.