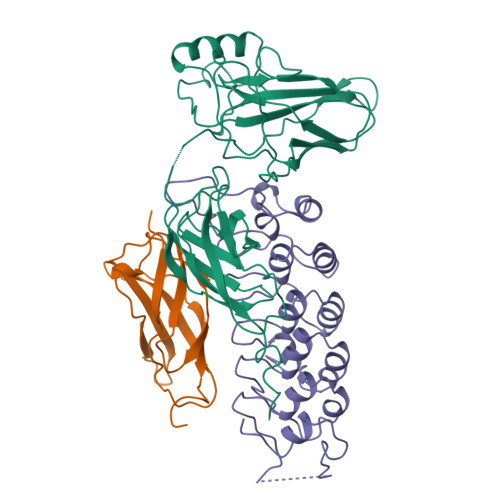
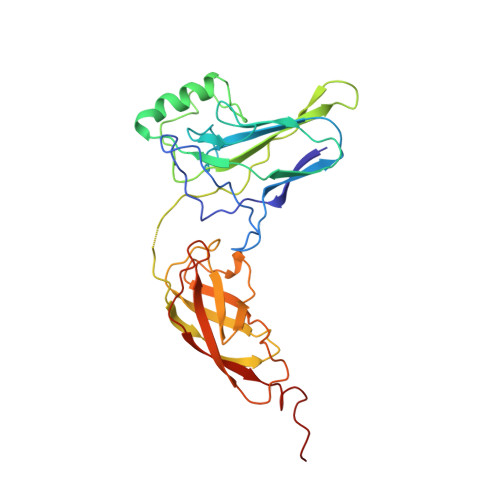
The crystal structure of the IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex reveals mechanisms of NF-kappaB inactivation.
Huxford, T., Huang, D.B., Malek, S., Ghosh, G.(1998) Cell 95: 759-770
- PubMed: 9865694
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81699-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IKN - PubMed Abstract:
IkappaBalpha regulates the transcription factor NF-kappaB through the formation of stable IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complexes. Prior to induction, IkappaBalpha retains NF-kappaB in the cytoplasm until the NF-kappaB activation signal is received. After activation, NF-kappaB is removed from gene promoters through association with nuclear IkappaBalpha, restoring the preinduction state. The 2.3 A crystal structure of IkappaBalpha in complex with the NF-kappaB p50/p65 heterodimer reveals mechanisms of these inhibitory activities. The presence of IkappaBalpha allows large en bloc movement of the NF-kappaB p65 subunit amino-terminal domain. This conformational change induces allosteric inhibition of NF-kappaB DNA binding. Amino acid residues immediately preceding the nuclear localization signals of both NF-kappaB p50 and p65 subunits are tethered to the IkappaBalpha amino-terminal ankyrin repeats, impeding NF-kappaB from nuclear import machinery recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla 92093-0359, USA.