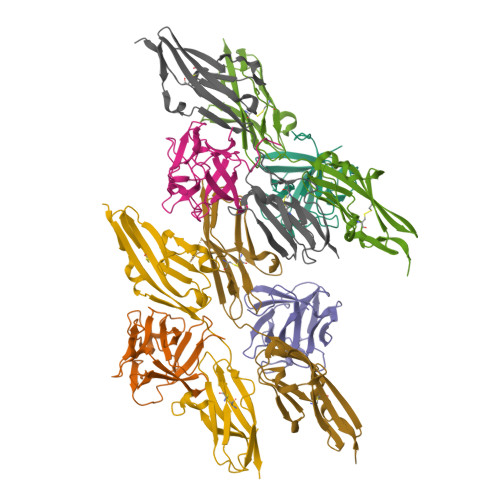
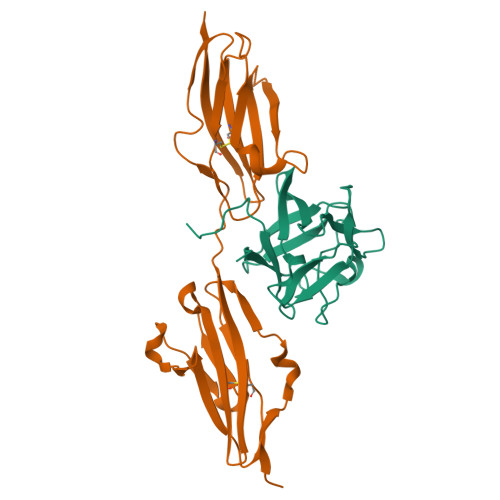
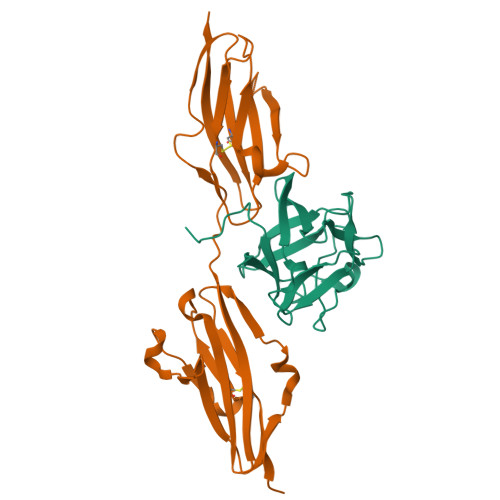
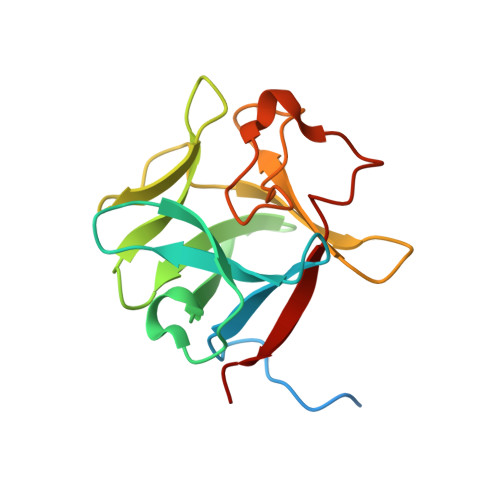
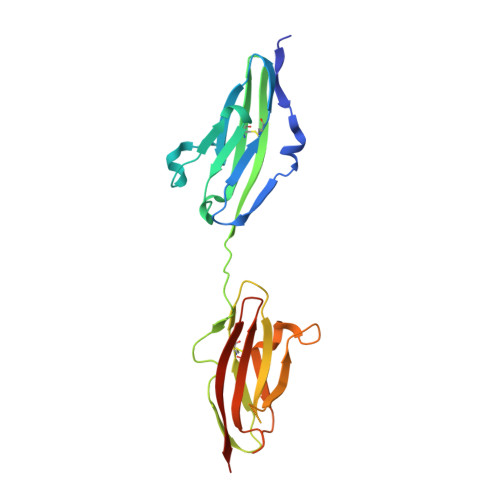
Structural basis for fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 activation in Apert syndrome.
Ibrahimi, O.A., Eliseenkova, A.V., Plotnikov, A.N., Yu, K., Ornitz, D.M., Mohammadi, M.(2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 7182-7187
- PubMed: 11390973
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.121183798
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1II4, 1IIL - PubMed Abstract:
Apert syndrome (AS) is characterized by craniosynostosis (premature fusion of cranial sutures) and severe syndactyly of the hands and feet. Two activating mutations, Ser-252 --> Trp and Pro-253 --> Arg, in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) account for nearly all known cases of AS. To elucidate the mechanism by which these substitutions cause AS, we determined the crystal structures of these two FGFR2 mutants in complex with fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2). These structures demonstrate that both mutations introduce additional interactions between FGFR2 and FGF2, thereby augmenting FGFR2-FGF2 affinity. Moreover, based on these structures and sequence alignment of the FGF family, we propose that the Pro-253 --> Arg mutation will indiscriminately increase the affinity of FGFR2 toward any FGF. In contrast, the Ser-252 --> Trp mutation will selectively enhance the affinity of FGFR2 toward a limited subset of FGFs. These predictions are consistent with previous biochemical data describing the effects of AS mutations on FGF binding. Alterations in FGFR2 ligand affinity and specificity may allow inappropriate autocrine or paracrine activation of FGFR2. Furthermore, the distinct gain-of-function interactions observed in each crystal structure provide a model to explain the phenotypic variability among AS patients.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY 10016, USA.