First structure of a snake venom metalloproteinase: a prototype for matrix metalloproteinases/collagenases.
Gomis-Ruth, F.X., Kress, L.F., Bode, W.(1993) EMBO J 12: 4151-4157
- PubMed: 8223430
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06099.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IAG - PubMed Abstract:
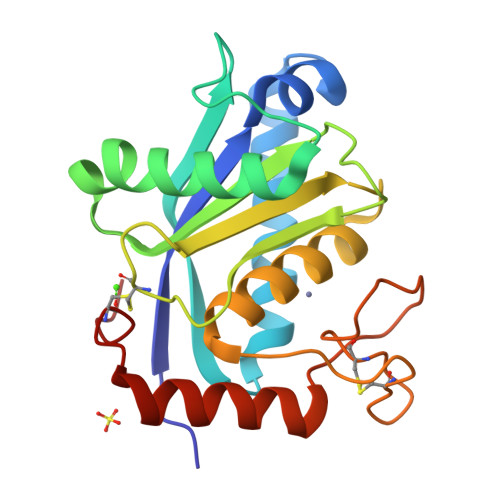
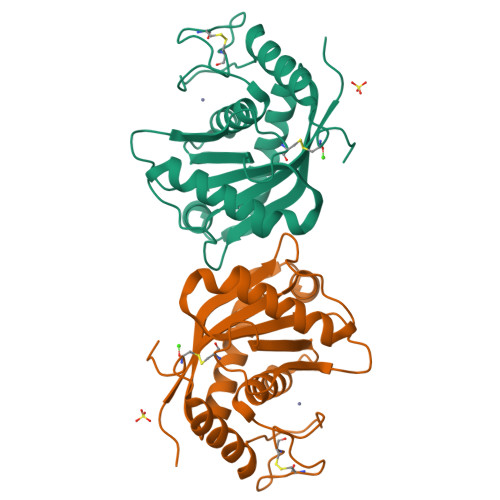
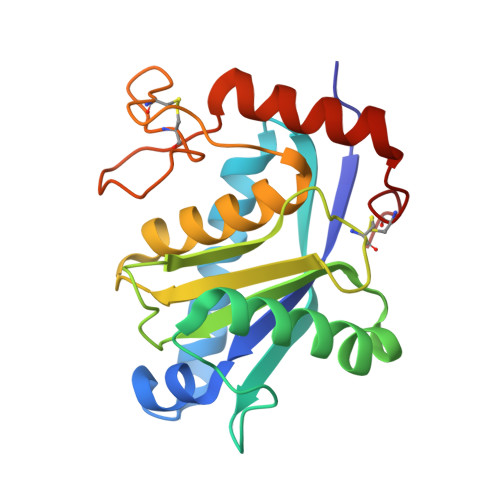
Adamalysin II, a 24 kDa zinc endopeptidase from the snake venom of Crotalus adamanteus, is a member of a large family of metalloproteinases isolated as small proteinases or proteolytic domains of mosaic haemorrhagic proteins from various snake venoms. Homologous domains have recently been detected in multimodular mammalian reproductive tract proteins. The 2.0 A crystal structure of adamalysin II reveals an ellipsoidal molecule with a shallow active-site cleft separating a relatively irregularly folded subdomain from the calcium-binding main molecular body composed of a five-stranded beta-sheet and four alpha-helices. The folding of the peptide fragment containing the zinc-binding motif HExxHxxGxxH bears only a distant resemblance to thermolysin, but is identical to that found in astacin, with the three histidines and a water molecule (linked to the glutamic acid) likewise constituting the zinc ligand; adamalysin II lacks a fifth (tyrosine) zinc ligand, however, leaving its zinc ion tetrahedrally co-ordinated. Furthermore, adamalysin II and astacin share an identical active-site basement formed by a common Metturn. Due to their virtually identical active-site environment and similar folding topology, the snake venom metalloproteinases (hitherto called adamalysins) and the astacins (and presumably also the matrix metalloproteinases/mammalian collagenases and the Serratia proteinase-like large bacterial proteinases) might be grouped into a common superfamily with distinct differences from the thermolysin family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, Martinsried, Germany.