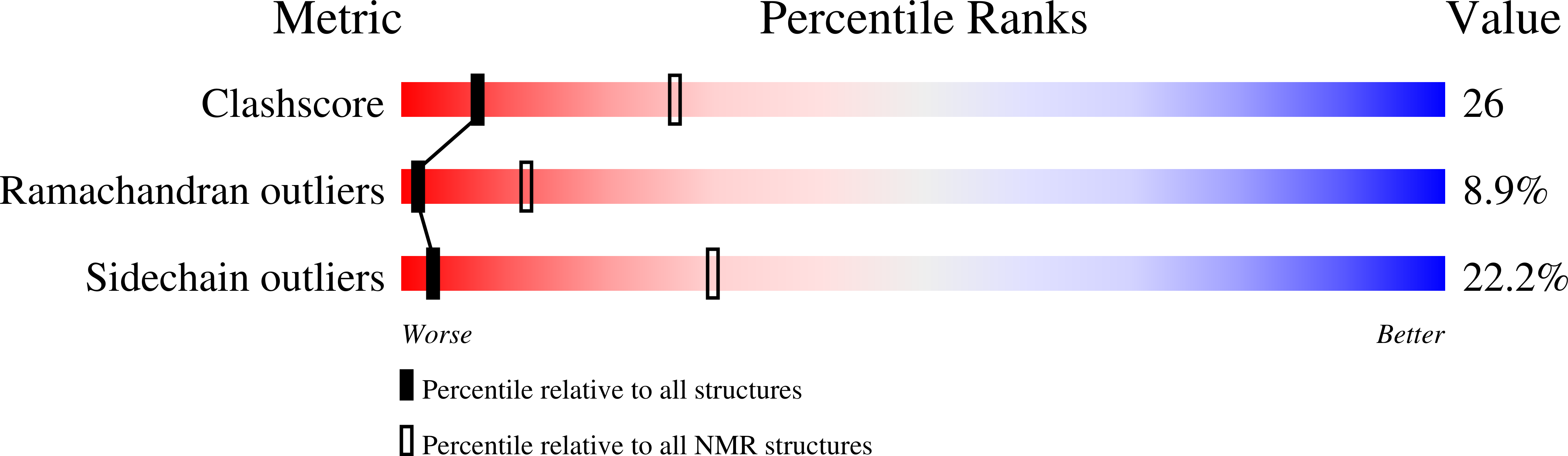Solution structures of the antifungal heliomicin and a selected variant with both antibacterial and antifungal activities.
Lamberty, M., Caille, A., Landon, C., Tassin-Moindrot, S., Hetru, C., Bulet, P., Vovelle, F.(2001) Biochemistry 40: 11995-12003
- PubMed: 11580275
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0103563
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1I2U, 1I2V - PubMed Abstract:
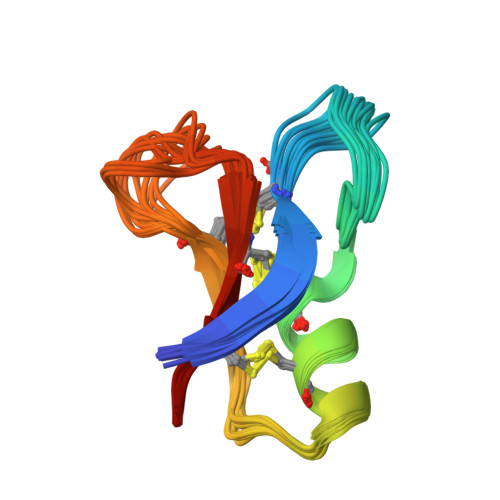
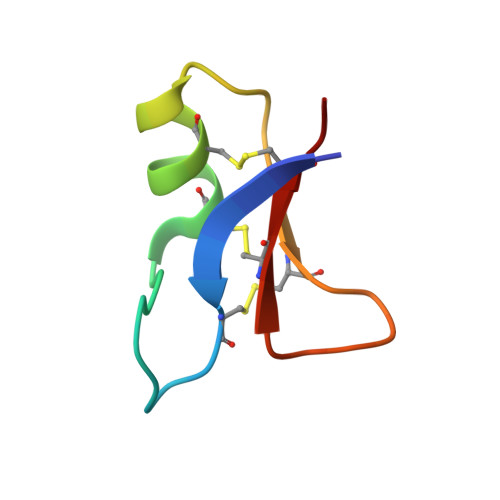
In response to an experimental infection, the lepidopteran Heliothis virescens produces an antifungal protein named heliomicin. Heliomicin displays sequence similarities with antifungal plant defensins and antibacterial or antifungal insect defensins. To gain information about the structural elements required for either antifungal or antibacterial activity, heliomicin and selected point-mutated variants were expressed in yeast as fusion proteins. The effects of mutations, defined by comparing the primary structure of heliomicin with the sequences of members of the insect defensin family, were analyzed using antibacterial and antifungal assays. One of the variants shows significant activity against Gram-positive bacteria while remaining efficient against fungi. The three-dimensional structures of this variant and of the wild-type protein were determined by two-dimensional (1)H NMR to establish a correlation between structure and antibacterial or antifungal activity. Wild-type and mutated heliomicins adopt a similar scaffold, including the so-called cysteine-stabilized alphabeta motif. A comparison of their structures with other defensin-type molecules indicates that common hydrophobic characteristics can be assigned to all the antifungal proteins. A comparative analysis of various structural features of heliomicin mutant and of antibacterial defensins enables common properties to be assessed, which will help to design new mutants with increased antibacterial activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Unité Propre de Recherche 9022, CNRS, "Réponse Immunitaire et Développement chez les Insectes", 15 rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg Cedex, France.