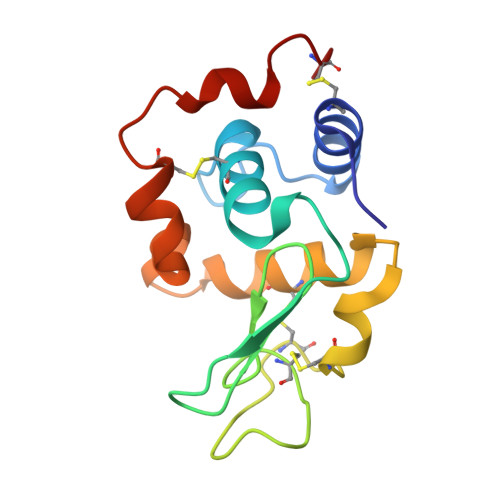
Structural and thermodynamic responses of mutations at a Ca2+ binding site engineered into human lysozyme.
Kuroki, R., Yutani, K.(1998) J Biological Chem 273: 34310-34315
- PubMed: 9852096
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.51.34310
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1I1Z, 1I20, 1I22 - PubMed Abstract:
Structural determinants of Ca2+ binding sites within proteins typically comprise several acidic residues in appropriate juxtaposition. Three residues (Ala-83, Gln-86, and Ala-92) in human lysozyme are characteristically mutated to Lys, Asp, and Asp, respectively, in natural Ca2+ binding lysozymes and alpha-lactalbumins. The effects of these mutations on the stability and Ca2+ binding properties of human lysozyme were investigated using calorimetry and were interpreted with crystal structures. The double mutant, in which Glu-86 and Ala-92 were replaced with Asp, clearly showed Ca2+ binding affinity, whereas neither point mutant showed Ca2+ affinity, indicating that both residues are essential. The further mutation of Ala-83 --> Lys did not affect the Ca2+ binding of the double mutant. The point mutations Ala-83 --> Lys and Glu-86 --> Asp did not affect the stability, whereas the mutation Ala-92 --> Asp was about 1.3 kcal/mol less stable. Structural analyses showed that both Asp-86 and Lys-83 were exposed to solvent. Side chains of Asp-86 and Asp-91 were rotated in opposite directions about chi1 angle, as if to reduce the electrostatic repulsion. The charged amino acids at the Ca2+ binding site did not significantly affect stability of the protein, possibly because of the local conformational change of the side chains.
Organizational Affiliation:
Central Laboratories for Key Technology, Kirin Brewery Co. Ltd., 1-13-5 Fukuura, Kanazawa-ku, Yokohama 236 Japan. r-kuroki@kirin.co.jp