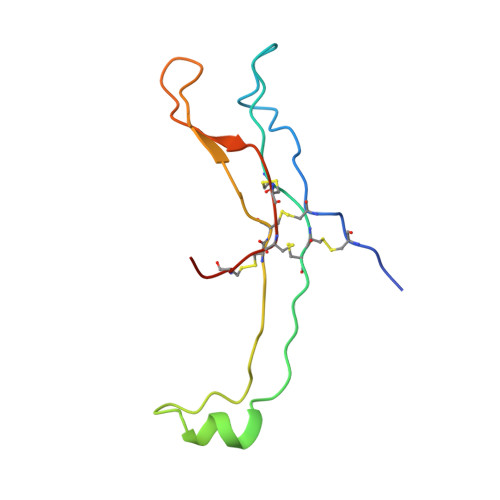
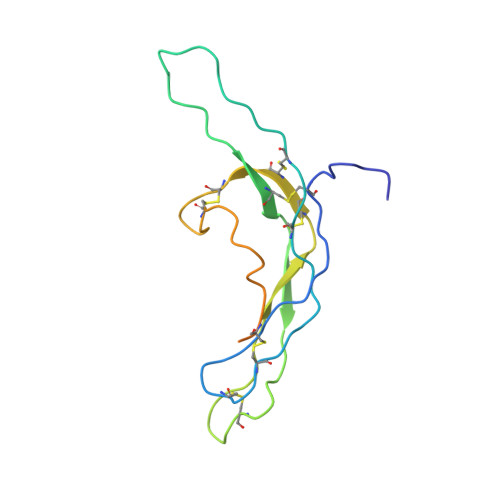
Crystal structure of human chorionic gonadotropin.
Lapthorn, A.J., Harris, D.C., Littlejohn, A., Lustbader, J.W., Canfield, R.E., Machin, K.J., Morgan, F.J., Isaacs, N.W.(1994) Nature 369: 455-461
- PubMed: 8202136
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/369455a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HRP - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional structure of human chorionic gonadotropin shows that each of its two different subunits has a similar topology, with three disulphide bonds forming a cystine knot. This same folding motif is found in some protein growth factors. The heterodimer is stabilized by a segment of the beta-subunit which wraps around the alpha-subunit and is covalently linked like a seat belt by the disulphide Cys 26-Cys 110. This extraordinary feature appears to be essential not only for the association of these heterodimers but also for receptor binding by the glycoprotein hormones.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Glasgow, UK.