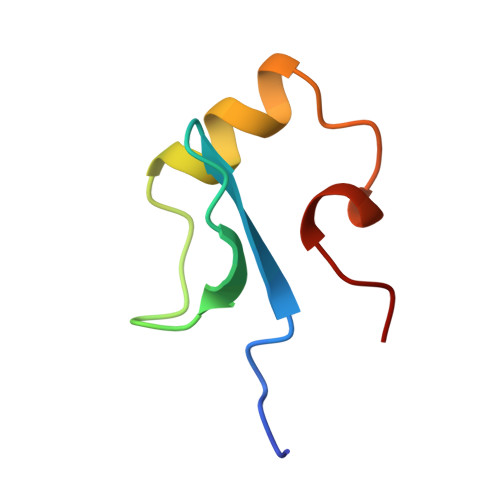
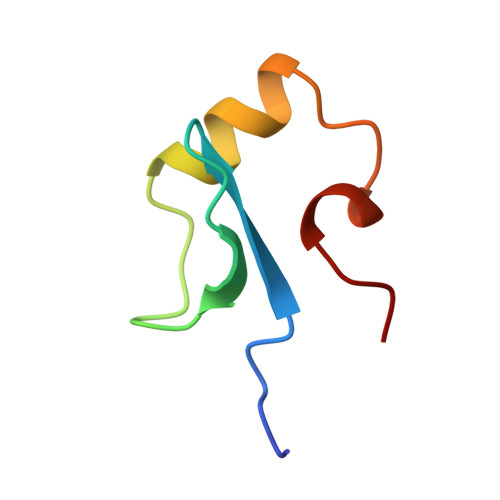
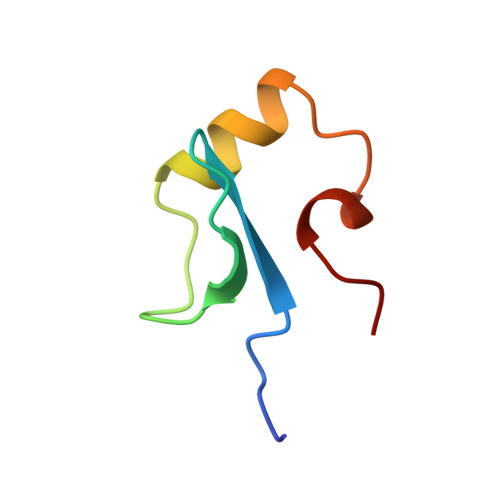
Solution structure of the DNA binding domain of a nucleoid-associated protein, H-NS, from Escherichia coli.
Shindo, H., Iwaki, T., Ieda, R., Kurumizaka, H., Ueguchi, C., Mizuno, T., Morikawa, S., Nakamura, H., Kuboniwa, H.(1995) FEBS Lett 360: 125-131
- PubMed: 7875316
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(95)00079-o
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HNR, 1HNS - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional structure of the C-terminal domain (47 residues) obtained from the hydrolysis of H-NS protein with bovine trypsin was determined by NMR measurements and distance geometry calculations. It is composed of an antiparallel beta-sheet, an alpha-helix and a 3(10)-helix which form a hydrophobic core, stabilizing the whole structure. This domain has been found to bind to DNA. Possible DNA binding sites are discussed on the basis of the solution structure of the C-terminal domain of H-NS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Science, Japan.