Crystallographic Analysis of Family 11 Endo-[Beta]-1,4-Xylanase Xyl1 from Streptomyces Sp. S38
Wouters, J., Georis, J., Engher, D., Vandenhaute, J., Dusart, J., Frere, J.M., Depiereux, E., Charlier, P.(2001) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 57: 1813
- PubMed: 11717493
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444901015153
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HIX - PubMed Abstract:
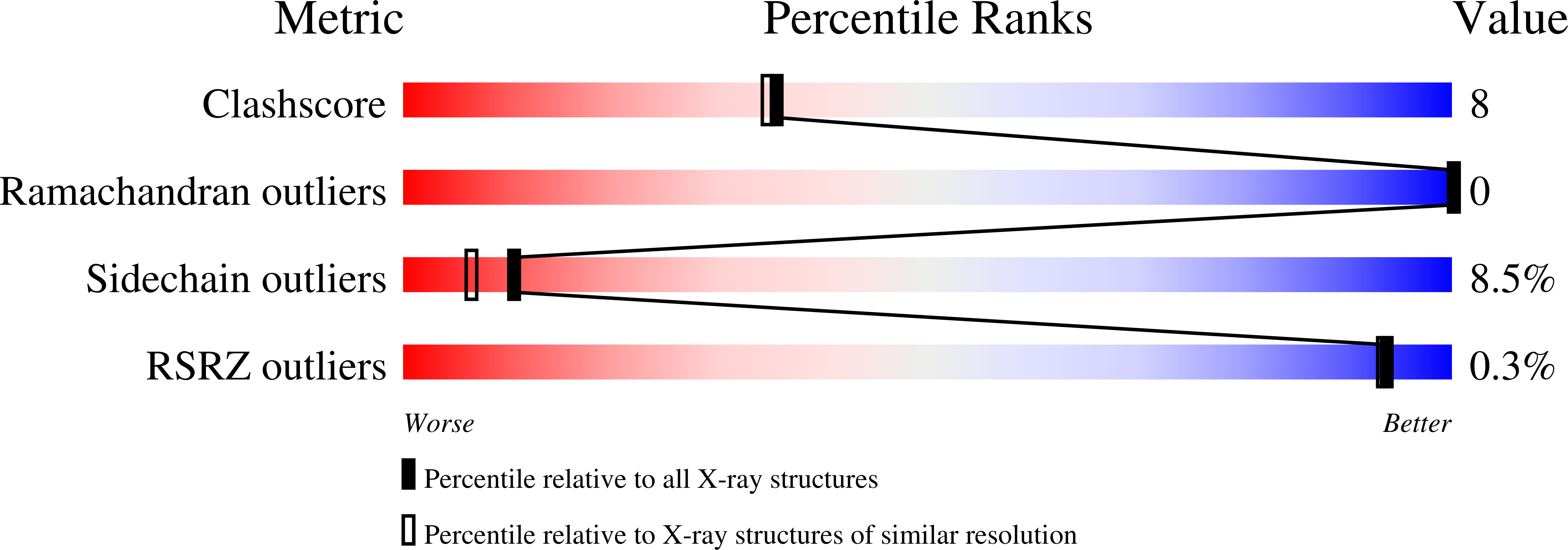
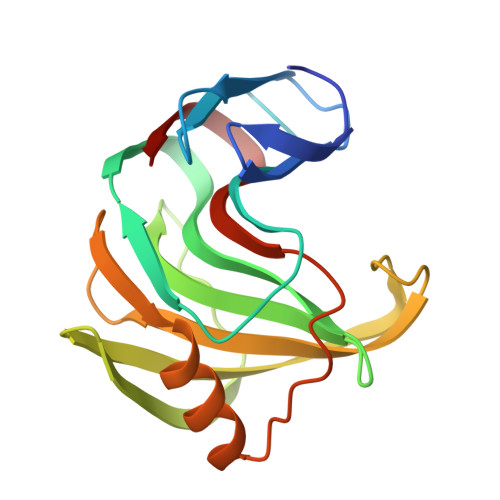
Family 11 endo-beta-1,4-xylanases degrade xylan, the main constituent of plant hemicelluloses, and have many potential uses in biotechnology. The structure of Xyl1, a family 11 endo-xylanase from Streptomyces sp. S38, has been solved. The protein crystallized from ammonium sulfate in the trigonal space group P321, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 71.49, c = 130.30 A, gamma = 120.0 degrees. The structure was solved at 2.0 A by X-ray crystallography using the molecular-replacement method and refined to a final R factor of 18.5% (R(free) = 26.9%). Xyl1 has the overall fold characteristic of family 11 xylanases, with two highly twisted beta-sheets defining a long cleft containing the two catalytic residues Glu87 and Glu177.
Organizational Affiliation:
Unité de Recherche en Biologie Moléculaire, Facultés Universitaires Notre Dame de la Paix, 61 Rue de Bruxelles, B-5000 Namur, Belgium. johan.wouters@fundp.ac.be