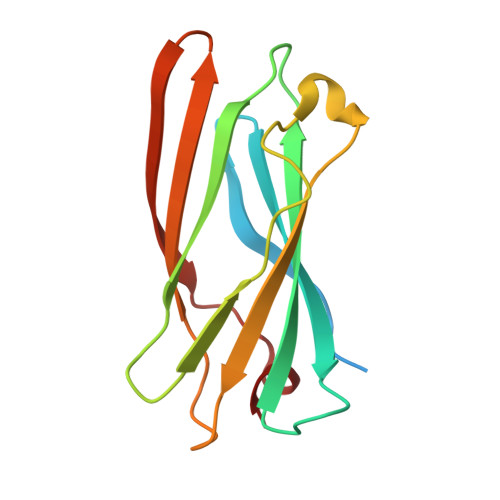
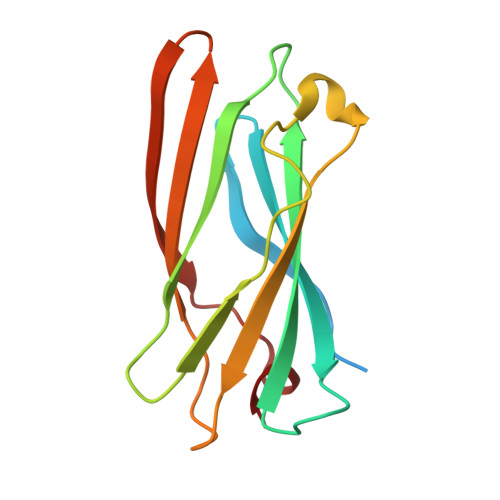
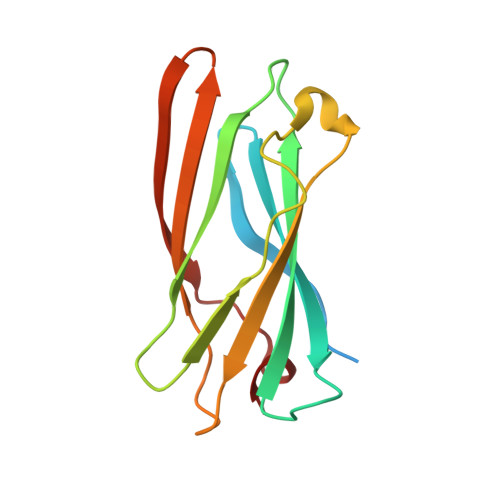
Gamma-Adaptin Appendage Domain. Structure and Binding Site for Eps15 and Gamma-Synergin
Kent, H.M., Mcmahon, H.M., Evans, P.R., Benmerah, A., Owen, D.J.(2002) Structure 10: 1139
- PubMed: 12176391
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00801-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GYU, 1GYV, 1GYW - PubMed Abstract:
The AP1 complex is one of a family of heterotetrameric clathrin-adaptor complexes involved in vesicular trafficking between the Golgi and endosomes. The complex has two large subunits, gamma and beta1, which can be divided into trunk, hinge, and appendage domains. The 1.8 A resolution structure of the gamma appendage is presented. The binding site for the known gamma appendage ligand gamma-synergin is mapped through creation of point mutations designed on the basis of the structure. We also show that Eps15, a protein believed to be involved in vesicle formation at the plasma membrane, is also a ligand of gamma appendage and binds to the same site as gamma-synergin. This observation explains the demonstrated brefeldinA (BFA)-sensitive colocalization of Eps15 and AP1 at the Golgi complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, United Kingdom.