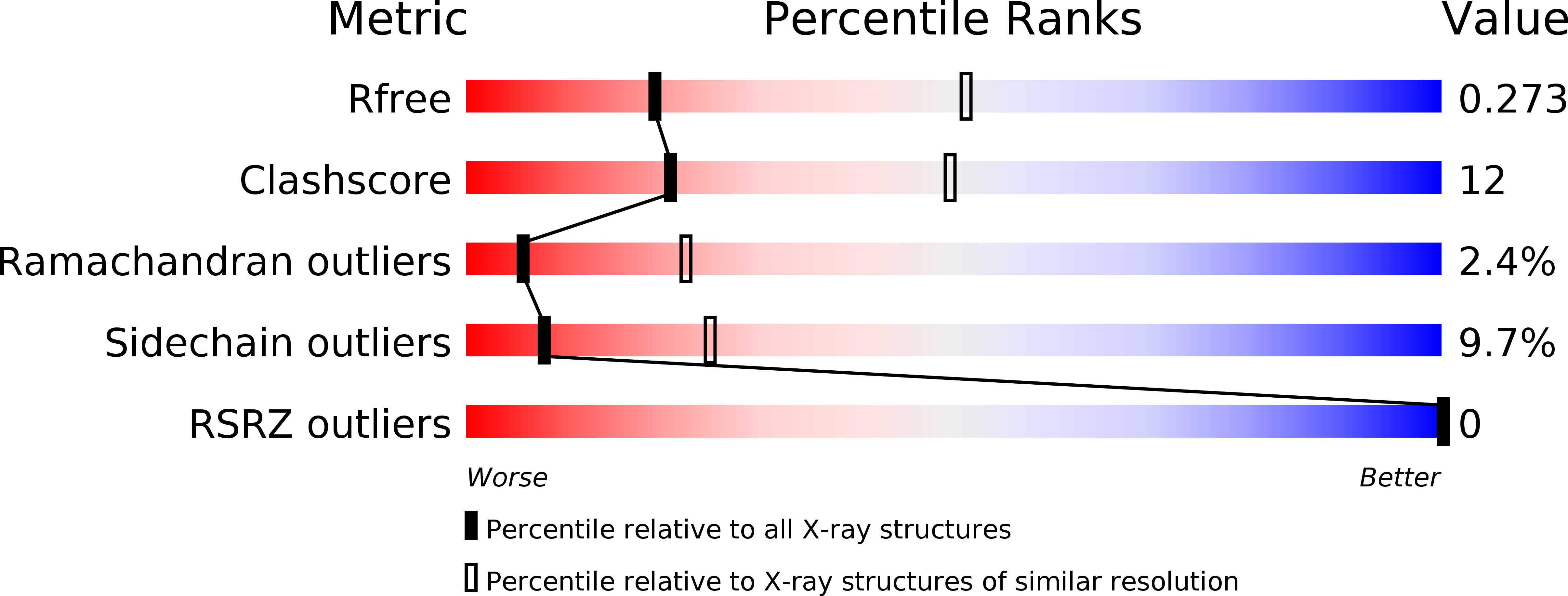
Structural basis of the membrane-targeting and unmasking mechanisms of the radixin FERM domain.
Hamada, K., Shimizu, T., Matsui, T., Tsukita, S., Hakoshima, T.(2000) EMBO J 19: 4449-4462
- PubMed: 10970839
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.17.4449
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GC6, 1GC7 - PubMed Abstract:
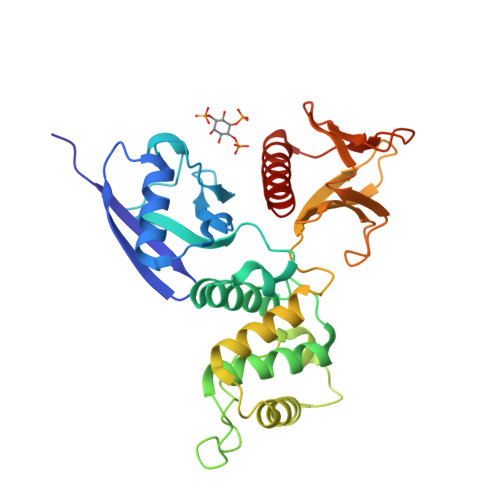
Radixin is a member of the ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) family of proteins, which play a role in the formation of the membrane-associated cytoskeleton by linking actin filaments and adhesion proteins. This cross-linking activity is regulated by phosphoinositides such as phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) in the downstream of the small G protein Rho. The X-ray crystal structures of the radixin FERM domain, which is responsible for membrane binding, and its complex with inositol-(1,4, 5)-trisphosphate (IP3) have been determined. The domain consists of three subdomains featuring a ubiquitin-like fold, a four-helix bundle and a phosphotyrosine-binding-like domain, respectively. These subdomains are organized by intimate interdomain interactions to form characteristic grooves and clefts. One such groove is negatively charged and so is thought to interact with basic juxta-membrane regions of adhesion proteins. IP3 binds a basic cleft that is distinct from those of pleckstrin homology domains and is located on a positively charged flat molecular surface, suggesting an electrostatic mechanism of plasma membrane targeting. Based on the structural changes associated with IP3 binding, a possible unmasking mechanism of ERM proteins by PIP2 is proposed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma, Nara 630-0101, Japan.