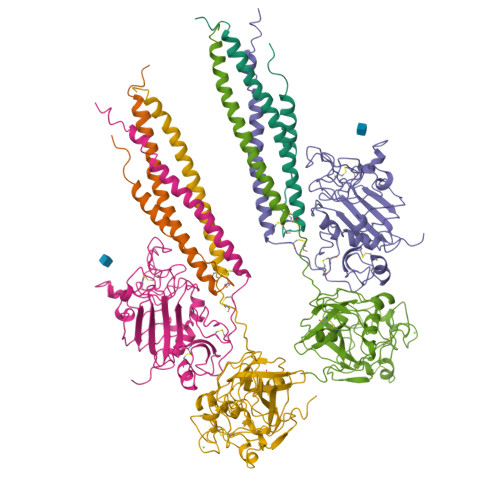
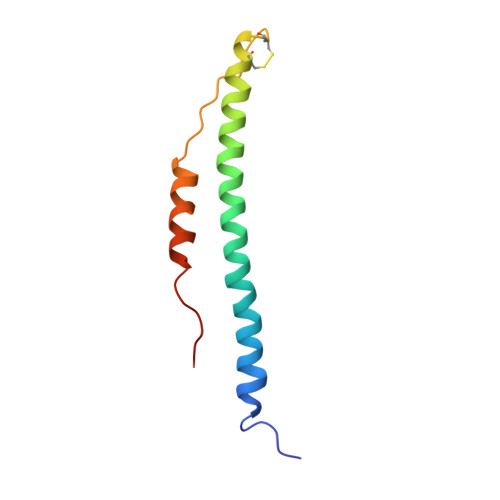
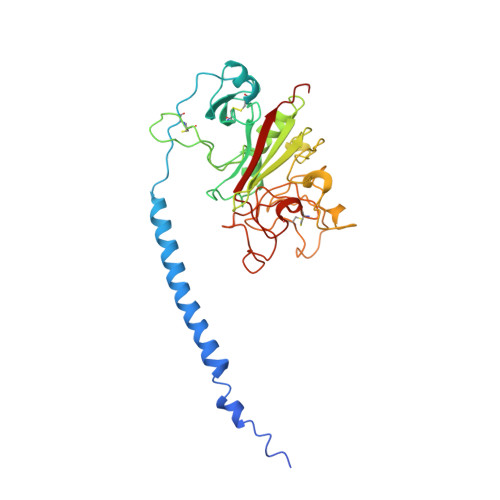
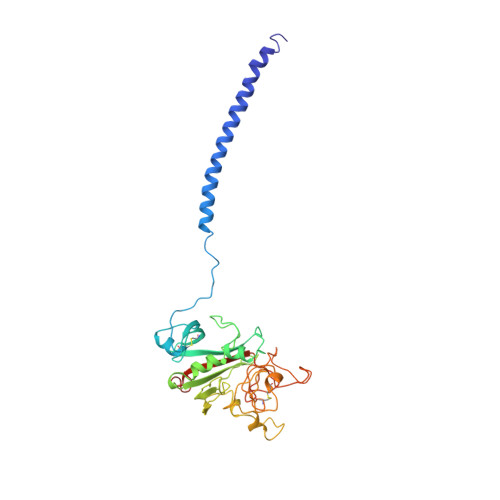
Crystal structures of fragment D from human fibrinogen and its crosslinked counterpart from fibrin.
Spraggon, G., Everse, S.J., Doolittle, R.F.(1997) Nature 389: 455-462
- PubMed: 9333233
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/38947
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FZA, 1FZB - PubMed Abstract:
In blood coagulation, units of the protein fibrinogen pack together to form a fibrin clot, but a crystal structure for fibrinogen is needed to understand how this is achieved. The structure of a core fragment (fragment D) from human fibrinogen has now been determined to 2.9 A resolution. The 86K three-chained structure consists of a coiled-coil region and two homologous globular entitles oriented at approximately 130 degrees to each other. Additionally, the covalently bound dimer of fragment D, known as 'double-D', was isolated from human fibrin, crystallized in the presence of a Gly-Pro-Arg-Pro-amide peptide ligand, which simulates the donor polymerization site, and its structure solved by molecular replacement with the model of fragment D.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Molecular Genetics, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla 92093-0634, USA.