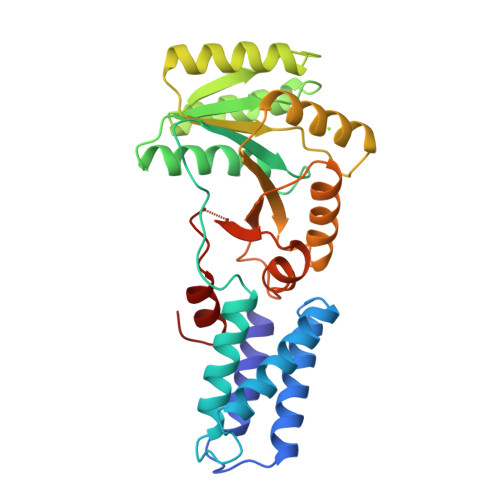
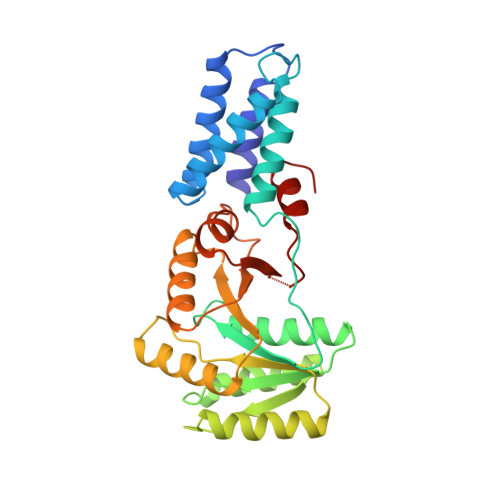
Structure of the conserved GTPase domain of the signal recognition particle.
Freymann, D.M., Keenan, R.J., Stroud, R.M., Walter, P.(1997) Nature 385: 361-364
- PubMed: 9002524
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385361a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FFH - PubMed Abstract:
The signal-recognition particle (SRP) and its receptor (SR) function in the co-translational targeting of nascent protein-ribosome complexes to the membrane translocation apparatus. The SRP protein subunit (termed Ffh in bacteria) that recognizes the signal sequence of nascent polypeptides is a GTPase, as is the SR-alpha subunit (termed FtsY). Ffh and FtsY interact directly, each stimulating the GTP hydrolysis activity of the other. The sequence of Ffh suggests three domains: an amino-terminal N domain of unknown function, a central GTPase G domain, and a methionine-rich M domain that binds both SRP RNA and signal peptides. Sequence conservation suggests that structurally similar N and G domains are present in FtsY. Here we report the structure of the nucleotide-free form of the NG fragment of Ffh. Consistent with a role for apo Ffh in protein targeting, the side chains of the empty active-site pocket form a tight network of interactions which may stabilize the nucleotide-free protein. The structural relationship between the two domains suggests that the N domain senses or controls the nucleotide occupancy of the GTPase domain. A structural subdomain unique to these evolutionarily conserved GTPases constitutes them as a distinct subfamily in the GTPase superfamily.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco 94143-0448, USA. freymann@msg.ucsf.edu