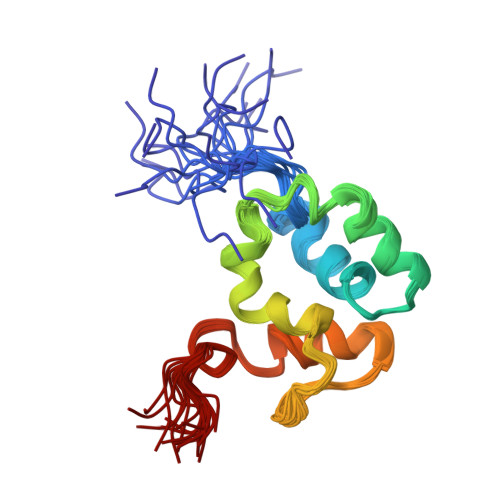
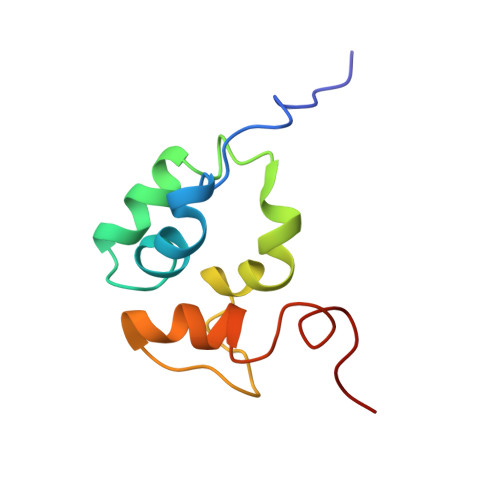
The solution structure of the C-terminal domain of the Mu B transposition protein.
Hung, L.H., Chaconas, G., Shaw, G.S.(2000) EMBO J 19: 5625-5634
- PubMed: 11060014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.21.5625
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1F6V - PubMed Abstract:
Mu B is one of four proteins required for the strand transfer step of bacteriophage Mu DNA transposition and the only one where no high resolution structural data is available. Structural work on Mu B has been hampered primarily by solubility problems and its tendency to aggregate. We have overcome this problem by determination of the three-dimensional structure of the C-terminal domain of Mu B (B(223-312)) in 1.5 M NaCl using NMR spectroscopic methods. The structure of Mu B(223-312) comprises four helices (backbone r.m.s.d. 0.46 A) arranged in a loosely packed bundle and resembles that of the N-terminal region of the replication helicase, DnaB. This structural motif is likely to be involved in the inter-domainal regulation of ATPase activity for both Mu A and DnaB. The approach described here for structural determination in high salt may be generally applicable for proteins that do not crystallize and that are plagued by solubility problems at low ionic strength.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and McLaughlin Macromolecular Structure Facility, The University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5C1. shaw@serena.biochem.uwo.ca