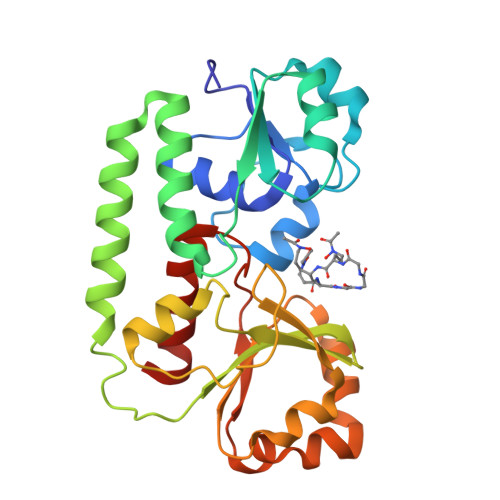
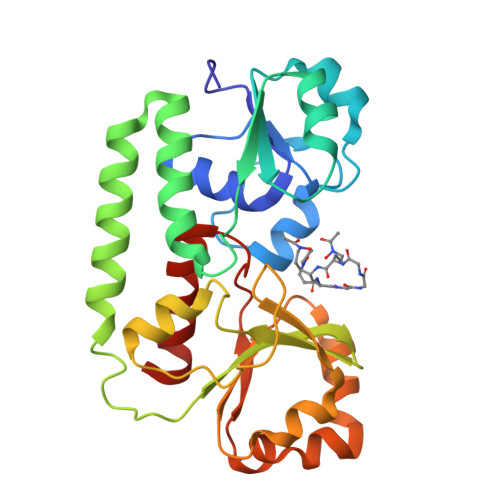
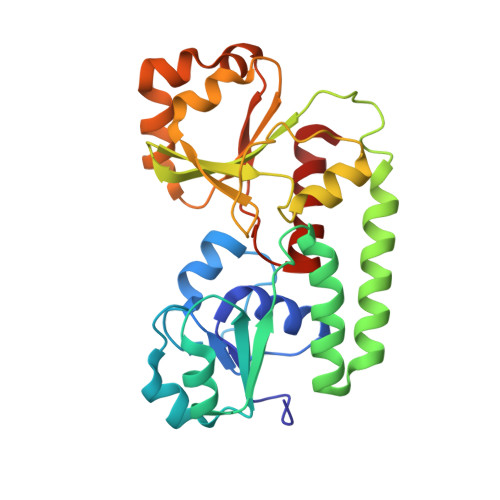
The structure of the ferric siderophore binding protein FhuD complexed with gallichrome.
Clarke, T.E., Ku, S.Y., Dougan, D.R., Vogel, H.J., Tari, L.W.(2000) Nat Struct Biol 7: 287-291
- PubMed: 10742172
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/74048
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EFD - PubMed Abstract:
Siderophore binding proteins play a key role in the uptake of iron in many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. FhuD is a soluble periplasmic binding protein that transports ferrichrome and other hydroxamate siderophores. The crystal structure of FhuD from Escherichia coli in complex with the ferrichrome homolog gallichrome has been determined at 1.9 ¿ resolution, the first structure of a periplasmic binding protein involved in the uptake of siderophores. Gallichrome is held in a shallow pocket lined with aromatic groups; Arg and Tyr side chains interact directly with the hydroxamate moieties of the siderophore. FhuD possesses a novel fold, suggesting that its mechanisms of ligand binding and release are different from other structurally characterized periplasmic ligand binding proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive N.W., Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 1N4.