Structural characterisation of the native fetuin-binding protein Scilla campanulata agglutinin: a novel two-domain lectin.
Wright, L.M., Reynolds, C.D., Rizkallah, P.J., Allen, A.K., Van Damme, E.J., Donovan, M.J., Peumans, W.J.(2000) FEBS Lett 468: 19-22
- PubMed: 10683433
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01109-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1DLP - PubMed Abstract:
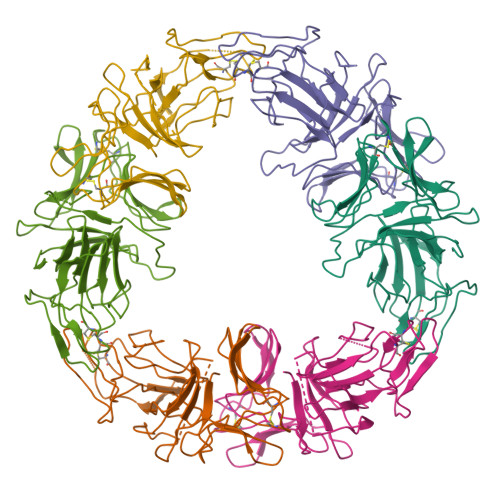
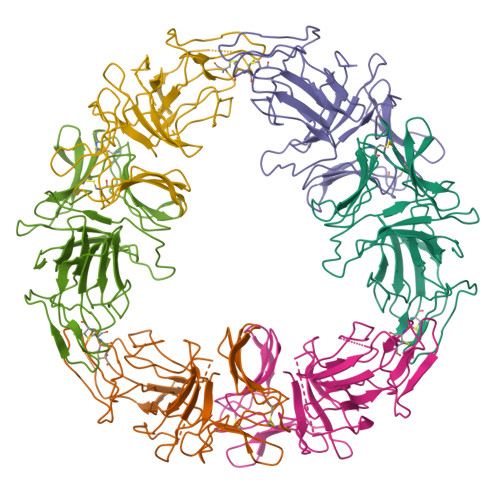
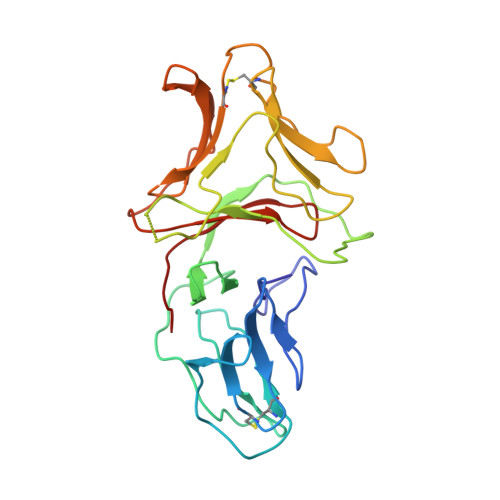
The three-dimensional structure of a 244-residue, multivalent, fetuin-binding lectin, SCAfet, isolated from bluebell (Scilla campanulata) bulbs, has been solved at 3.3 A resolution by molecular replacement using the coordinates of the 119-residue, mannose-binding lectin, SCAman, also from bluebell bulbs. Unlike most monocot mannose-binding lectins, such as Galanthus nivalis agglutinin from snowdrop bulbs, which fold into a single domain, SCAfet contains two domains with approximately 55% sequence identity, joined by a linker peptide. Both domains are made up of a 12-stranded beta-prism II fold, with three putative carbohydrate-binding sites, one on each subdomain. SCAfet binds to the complex saccharides of various animal glycoproteins but not to simple sugars.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biomolecular Sciences, Max Perutz Building, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool, UK.