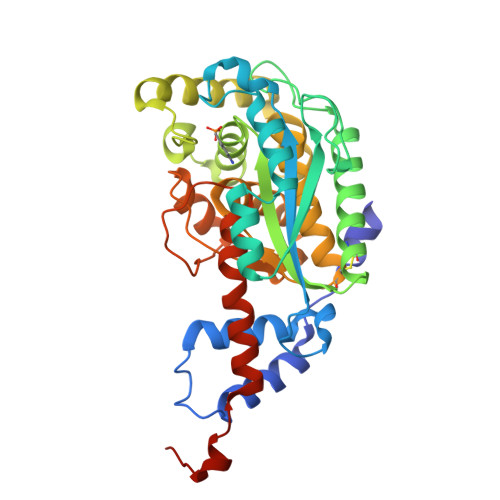
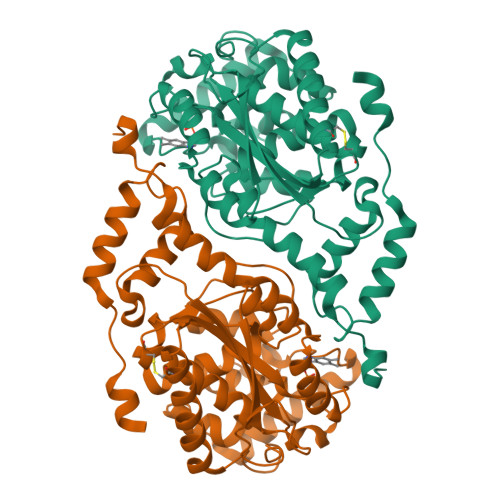
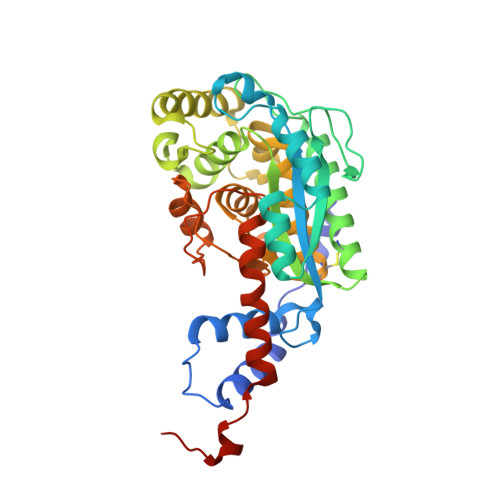
The three-dimensional structures of nicotinate mononucleotide:5,6- dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase (CobT) from Salmonella typhimurium complexed with 5,6-dimethybenzimidazole and its reaction products determined to 1.9 A resolution.
Cheong, C.G., Escalante-Semerena, J.C., Rayment, I.(1999) Biochemistry 38: 16125-16135
- PubMed: 10587435
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi991752c
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1D0S, 1D0V - PubMed Abstract:
Nicotinate mononucleotide:5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase (CobT) from Salmonella typhimurium plays a central role in the synthesis of alpha-ribazole, which is a key component of the lower ligand of cobalamin. Two X-ray structures of CobT are reported here at 1.9 A resolution. First, a complex of CobT with 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole, and second, a complex of CobT with its reaction products, nicotinate and alpha-ribazole-5'-phosphate. CobT was cocrystallized with 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) in the space group P2(1)2(1)2 with unit cell dimensions of a = 72.1 A, b = 90.2 A, and c = 47.5 A and one protomer per asymmetric unit. Subsequently, the crystals containing DMB were soaked in nicotinate mononucleotide whereupon the physiological reaction occurred in the crystal lattice to yield nicotinate and alpha-ribazole-5'-phosphate. These studies show that CobT is a dimer where each subunit consists of two domains. The large domain is dominated by a parallel six-stranded beta-sheet with connecting alpha-helices that exhibit the topology of a Rossmann fold. The small domain is made from components of the N- and C-terminal sections of the polypeptide chain and contains a three-helix bundle. The fold of CobT is unrelated to the type I and II phosphoribosylpyrophosphate dependent transferases and does not appear to be related to any other protein whose structure is known. The enzyme active site is located in a large cavity formed by the loops at the C-terminal ends of the beta-strands and the small domain of the neighboring subunit. DMB binds in a hydrophobic pocket created in part by the neighboring small domain. This is consistent with the broad specificity of this enzyme for aromatic substrates [Trzebiatowski, J. R., Escalante-Semerena (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 17662-17667]. The binding site for DMB suggests that Glu317 is the catalytic base required for the reaction. The remainder of the cavity binds the nicotinate and ribose-5'-phosphate moieties, which are nestled within the loops at the ends of the beta-strands. Interestingly, the orientation of the substrate and products are opposite from that expected for a Rossmann fold.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Enzyme Research, Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin, Madison 53705, USA.