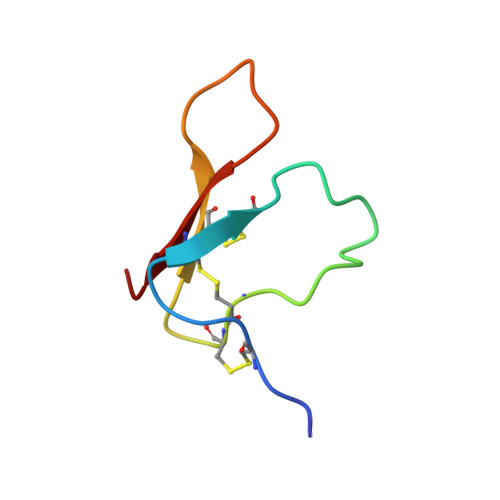
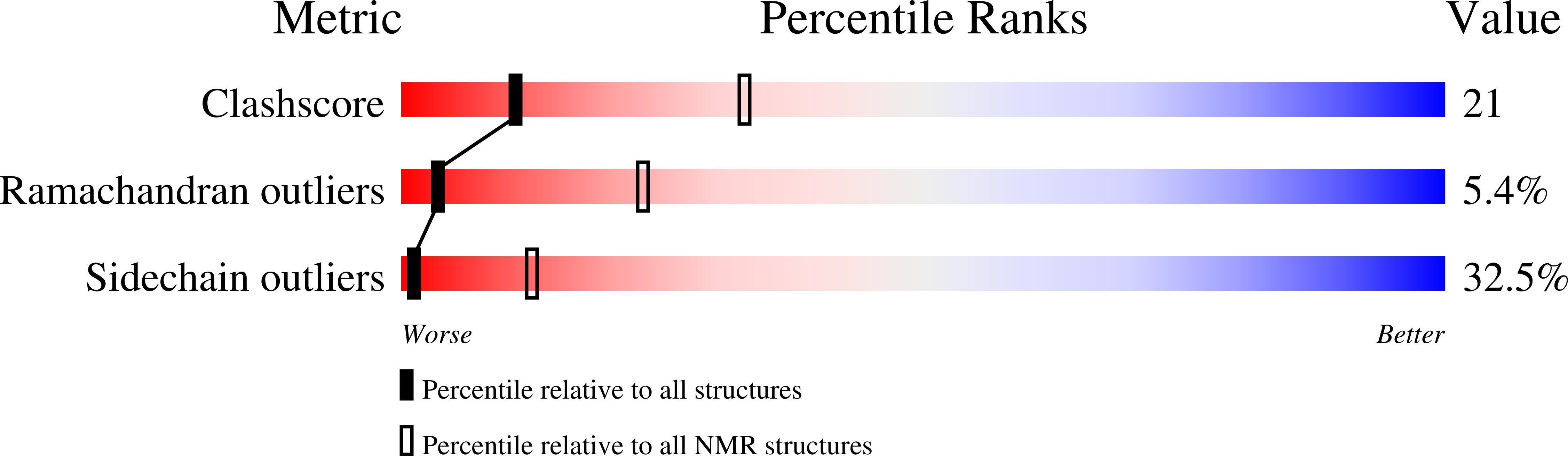Structure of the antimicrobial peptide tachystatin A.
Fujitani, N., Kawabata, S., Osaki, T., Kumaki, Y., Demura, M., Nitta, K., Kawano, K.(2002) J Biol Chem 277: 23651-23657
- PubMed: 11959852
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111120200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1CIX - PubMed Abstract:
The solution structure of antimicrobial peptide tachystatin A from the Japanese horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) was determined by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance measurements and distance-restrained simulated annealing calculations. The correct pairs of disulfide bonds were also confirmed in this study. The obtained structure has a cysteine-stabilized triple-stranded beta-sheet as a dominant secondary structure and shows an amphiphilic folding observed in many membrane-interactive peptides. Interestingly, tachystatin A shares structural similarities with the calcium channel antagonist omega-agatoxin IVA isolated from spider toxin and mammalian defensins, and we predicted that omega-agatoxin IVA also have the antifungal activity. These structural comparisons and functional correspondences suggest that tachystatin A and omega-agatoxin IVA may exert the antimicrobial activity in a manner similar to defensins, and we have confirmed such activity using fungal culture assays. Furthermore, tachystatin A is a chitin-binding peptide, and omega-agatoxin IVA also showed chitin-binding activities in this study. Tachystatin A and omega-agatoxin IVA showed no structural homology with well known chitin-binding motifs, suggesting that their structures belong to a novel family of chitin-binding peptides. Comparison of their structures with those of cellulose-binding proteins indicated that Phe(9) of tachystatin A might be an essential residue for binding to chitin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan.