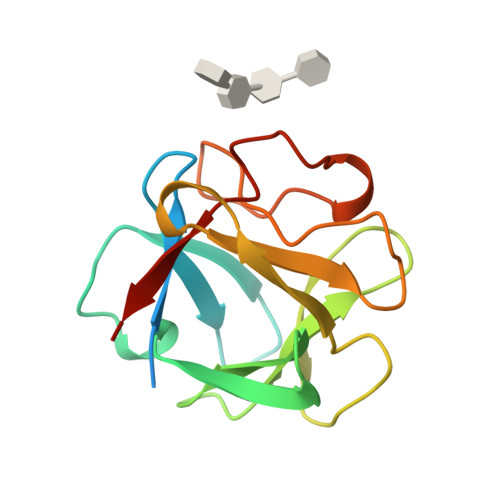
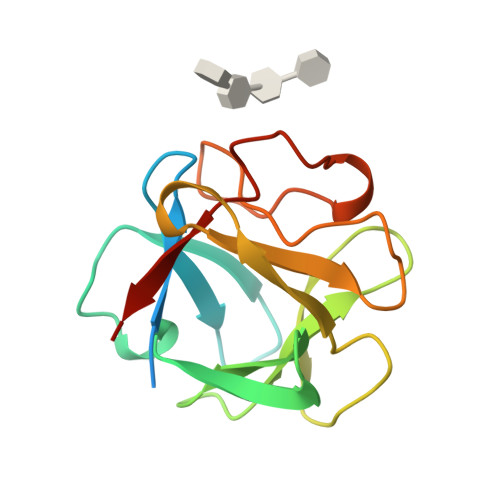
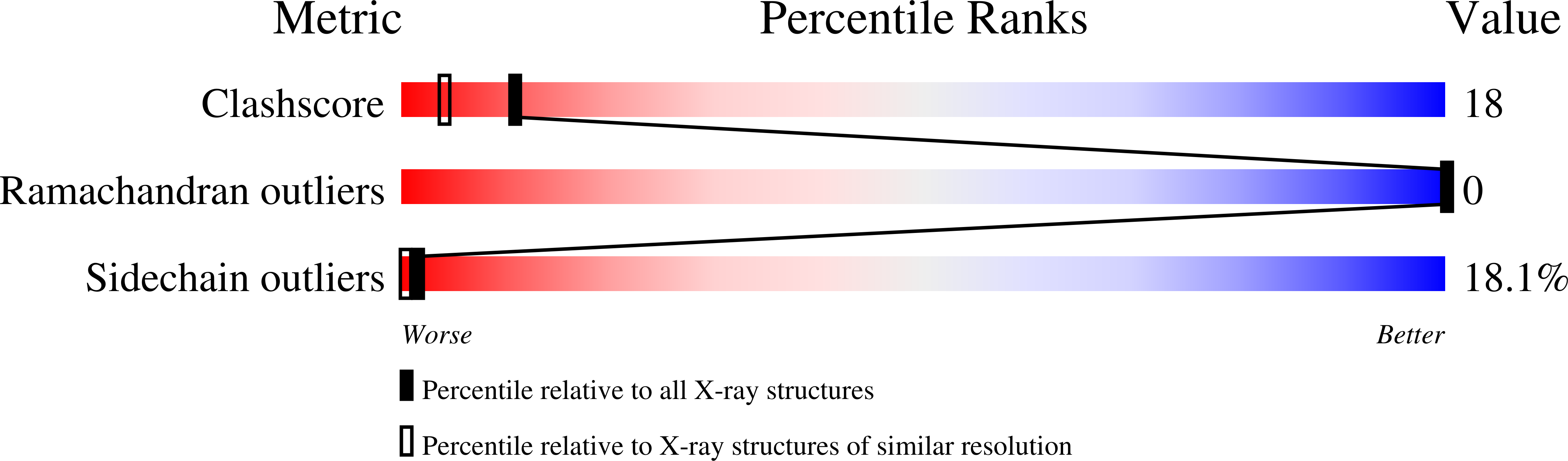Heparin structure and interactions with basic fibroblast growth factor.
Faham, S., Hileman, R.E., Fromm, J.R., Linhardt, R.J., Rees, D.C.(1996) Science 271: 1116-1120
- PubMed: 8599088
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.271.5252.1116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BFB, 1BFC - PubMed Abstract:
Crystal structures of heparin-derived tetra- and hexasaccharides complexed with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) were determined at resolutions of 1.9 and 2.2 angstroms, respectively. The heparin structure may be approximated as a helical polymer with a disaccharide rotation of 174 degrees and a translation of 8.6 angstroms along the helix axis. Both molecules bound similarly to a region of the bFGF surface containing residues asparagine-28, arginine-121, lysine-126, and glutamine-135, the hexasaccharide also interacted with an additional binding site formed by lysine-27, asparagine-102, and lysine-136. No significant conformational change in bFGF occurred upon heparin oligosaccharide binding, which suggests that heparin primarily serves to juxtapose components of the FGF signal transduction pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA.