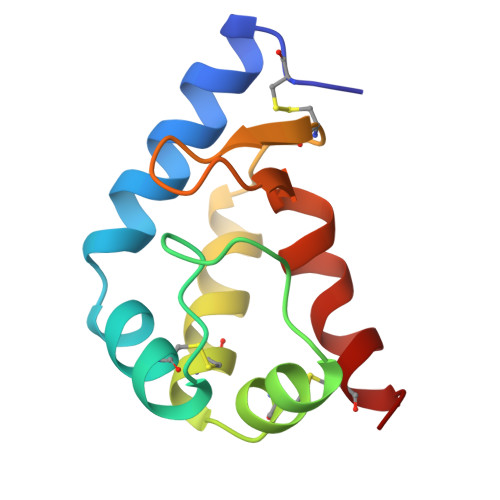
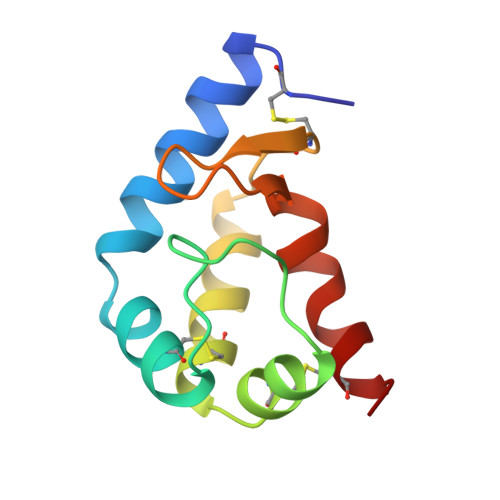
Crystal structure of a fungal elicitor secreted by Phytophthora cryptogea, a member of a novel class of plant necrotic proteins.
Boissy, G., de La Fortelle, E., Kahn, R., Huet, J.C., Bricogne, G., Pernollet, J.C., Brunie, S.(1996) Structure 4: 1429-1439
- PubMed: 8994969
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00150-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BEO - PubMed Abstract:
Elicitins form a novel class of plant necrotic proteins which are secreted by Phytophthora and Pythium fungi, parasites of many economically important crops. These proteins induce leaf necrosis in infected plants and elicit an incompatible hypersensitive-like reaction, leading to the development of a systemic acquired resistance against a range of fungal and bacterial plant pathogens. No crystal structures of this class of protein are available. The crystal structure determination of beta-cryptogein (CRY), secreted by Phytophthora cryptogea, was undertaken to identify structural features important for the necrotic activity of elicitins. The structure of CRY was determined using the multiwavelength anomalous diffraction technique and refined to 2.2 A resolution. The overall structure has a novel fold consisting of six alpha helices and a beak-like motif, whose sequence is highly conserved within the family, composed of an antiparallel two-stranded beta sheet and an omega loop. This motif is assumed to be a major recognition site for a putative receptor and/or ligand. Two other distinct binding sites seem to be correlated to the level of necrotic activity of elicitins. The determination of the crystal structure of a member of the elicitin family may make it possible to separate the activity that causes leaf necrosis from that inducing systemic acquired resistance to pathogens, making it feasible to engineer a non-toxic elicitin that only elicits plant defences. Such studies should aid the development of non-toxic agricultural pest control.
Organizational Affiliation:
Unité de Recherche Biochimie & Structure des Protéines, INRA, Jouy-en-Josas, France.