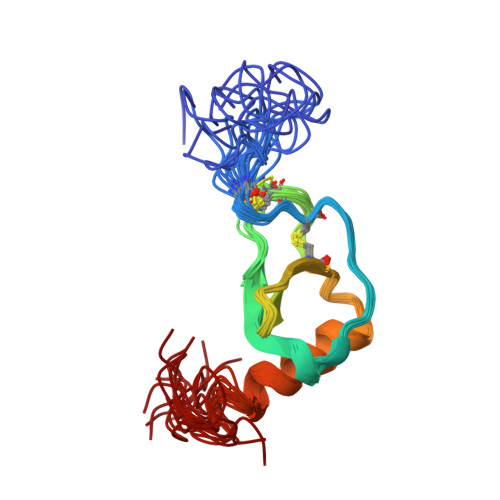
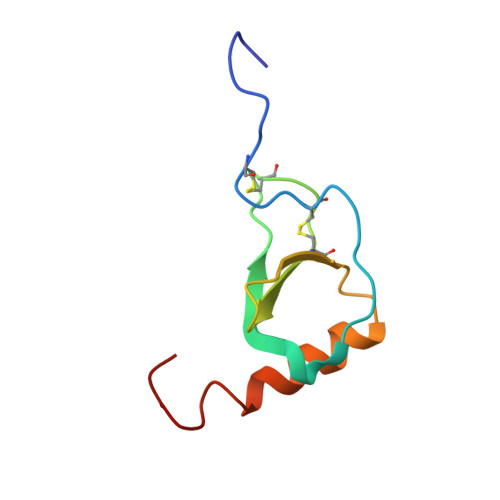
Solution structure and dynamics of the CX3C chemokine domain of fractalkine and its interaction with an N-terminal fragment of CX3CR1.
Mizoue, L.S., Bazan, J.F., Johnson, E.C., Handel, T.M.(1999) Biochemistry 38: 1402-1414
- PubMed: 9931005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9820614
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1B2T - PubMed Abstract:
Fractalkine, a novel CX3C chemokine, is unusual because of both its membrane-associated structure and its direct role in cell adhesion. We have solved the solution structure of the chemokine domain of fractalkine (residues 1-76) by heteronuclear NMR methods. The 20 lowest energy structures in the ensemble have an average backbone rmsd of 0.43 A, excluding the termini. In contrast to many other chemokines which form homodimers, fractalkine's chemokine module is monomeric. Comparison of the structure to CC and CXC chemokines reveals interesting differences which are likely to be relevant to receptor binding. These include a bulge formed by the CX3C motif, the relative orientation of the N-terminus and 30's loop (residues 30-38), and the conformation of the N-loop (residues 9-19). 15N backbone relaxation experiments indicate that these same regions of the protein are dynamic. We also titrated 15N-labeled protein with a peptide from the N-terminus of the receptor CX3CR1 and confirmed that this region of the receptor contacts the fractalkine chemokine domain. Interestingly, the binding site maps roughly to the regions of greatest flexibility and structural variability. Together, these data provide a first glimpse of how fractalkine interacts with its receptor and should help guide mutagenesis studies to further elucidate the molecular details of binding and signaling through CX3CR1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California at Berkeley 94720, USA.