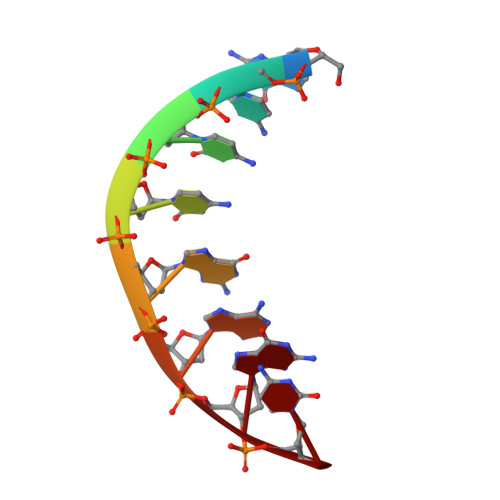
A DNA Structure Containing AgI -Mediated G:G and C:C Base Pairs
Liu, H.H., Shen, F.S., Haruehanroengra, P., Yao, Q.Q., Cheng, Y.S., Chen, Y.Q., Yang, C., Zhang, J., Wu, B.X., Luo, Q., Cui, R.X., Li, J.X., Ma, J.B., Sheng, J., Gan, J.H.(2017) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56: 9430-9434
- PubMed: 28635152
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201704891
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XJZ, 5XK0, 5XK1 - PubMed Abstract:
Metal-mediated base pairs have been extensively utilized in many research fields, including genetic-code extension, novel therapeutics development, and nanodevice design. Compared to other cations, Ag I is more flexible in pairing with natural base pairs. Herein, we present a DNA structure containing two C-Ag I -C pairs and the first reported G-Ag I -G pair in a short 8mer DNA strand. This structure not only provides detailed insight into these Ag I -mediated base-pairing patterns in DNA, but also represents the first nonhelical DNA structure driven by heavy-metal ions, thus further contributing to the structural diversity of DNA. This unique complex structure is highly sequence-dependent, thus implying functional potentials as a new DNA aptamer that can bind and recognize silver ions. These results not only advance our understanding of the interactions between Ag I and nucleobases, but also provide a unique structural component for the rational design of new DNA nanodevices.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Collaborative Innovation Center of Genetics and Development, Department of Physiology and Biophysics, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200433, China.