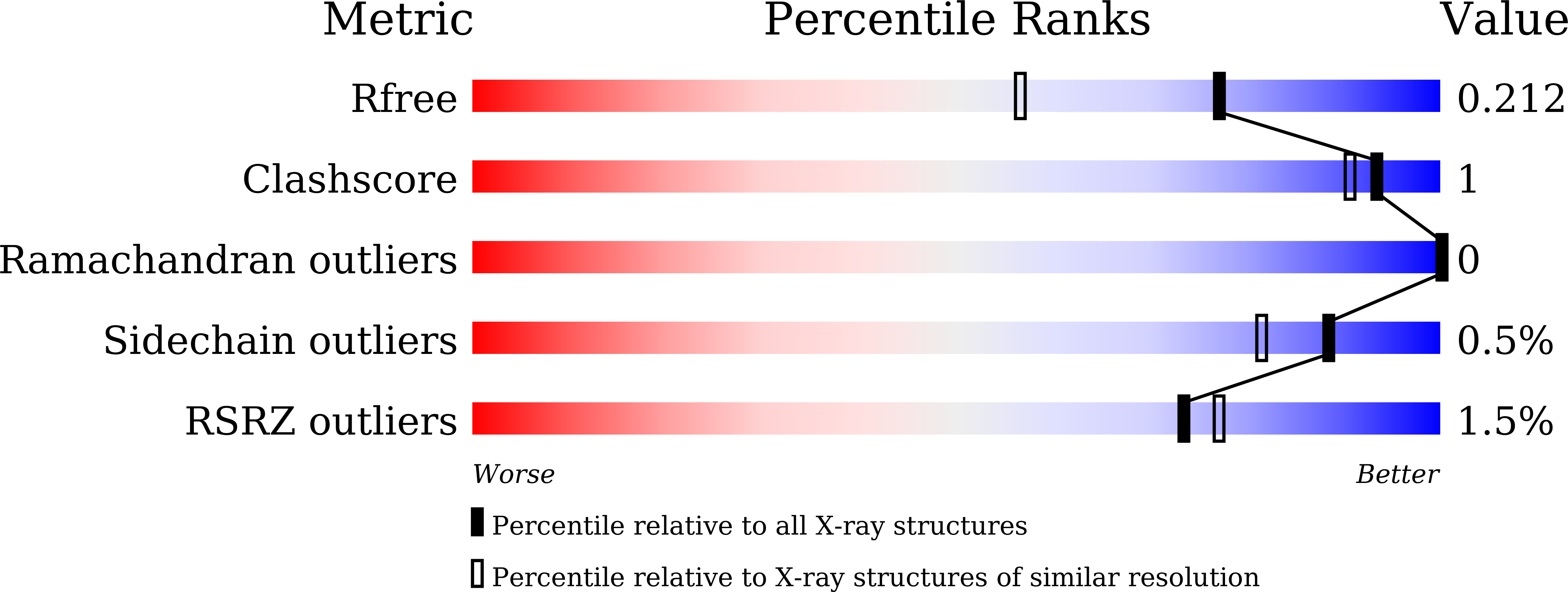
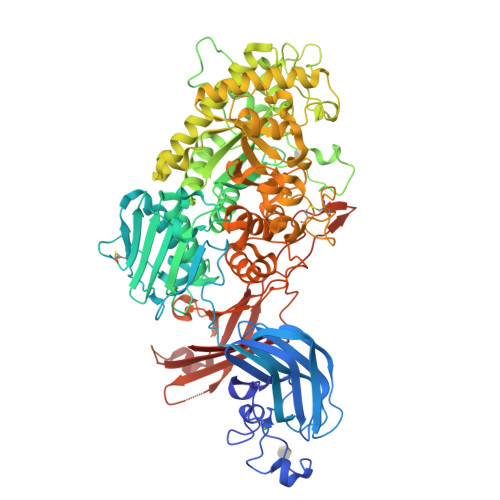
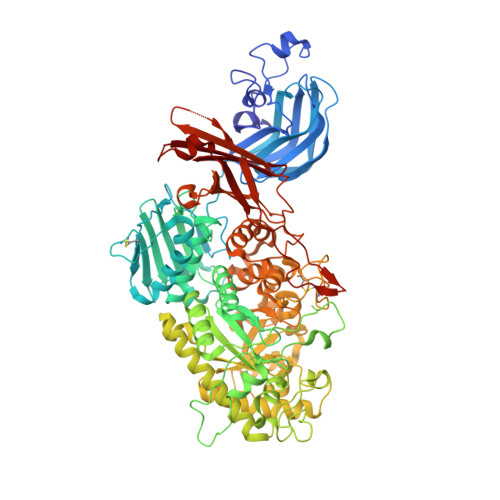
A bacterial sulfoglycosidase highlights mucin O-glycan breakdown in the gut ecosystem.
Katoh, T., Yamada, C., Wallace, M.D., Yoshida, A., Gotoh, A., Arai, M., Maeshibu, T., Kashima, T., Hagenbeek, A., Ojima, M.N., Takada, H., Sakanaka, M., Shimizu, H., Nishiyama, K., Ashida, H., Hirose, J., Suarez-Diez, M., Nishiyama, M., Kimura, I., Stubbs, K.A., Fushinobu, S., Katayama, T.(2023) Nat Chem Biol 19: 778-789
- PubMed: 36864192
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-023-01272-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WDT, 7WDU - PubMed Abstract:
Mucinolytic bacteria modulate host-microbiota symbiosis and dysbiosis through their ability to degrade mucin O-glycans. However, how and to what extent bacterial enzymes are involved in the breakdown process remains poorly understood. Here we focus on a glycoside hydrolase family 20 sulfoglycosidase (BbhII) from Bifidobacterium bifidum, which releases N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate from sulfated mucins. Glycomic analysis showed that, in addition to sulfatases, sulfoglycosidases are involved in mucin O-glycan breakdown in vivo and that the released N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate potentially affects gut microbial metabolism, both of which were also supported by a metagenomic data mining analysis. Enzymatic and structural analysis of BbhII reveals the architecture underlying its specificity and the presence of a GlcNAc-6S-specific carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) 32 with a distinct sugar recognition mode that B. bifidum takes advantage of to degrade mucin O-glycans. Comparative analysis of the genomes of prominent mucinolytic bacteria also highlights a CBM-dependent O-glycan breakdown strategy used by B. bifidum.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Biostudies, Kyoto University, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan.