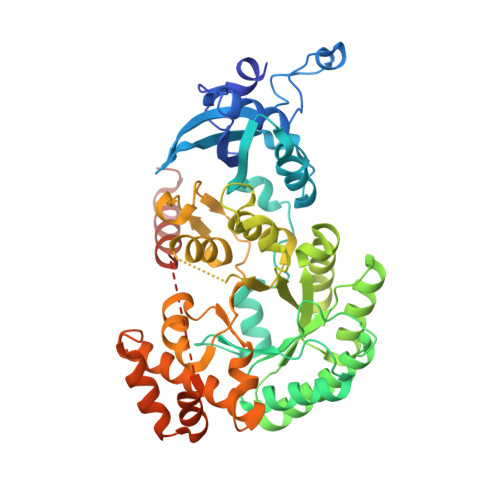
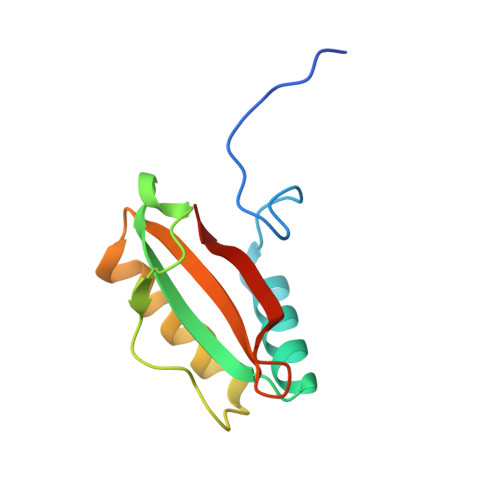
Multivalent interactions between CsoS2 and Rubisco mediate alpha-carboxysome formation.
Oltrogge, L.M., Chaijarasphong, T., Chen, A.W., Bolin, E.R., Marqusee, S., Savage, D.F.(2020) Nat Struct Mol Biol 27: 281-287
- PubMed: 32123388
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-020-0387-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6UEW - PubMed Abstract:
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments that function as the centerpiece of the bacterial CO 2 -concentrating mechanism by facilitating high CO 2 concentrations near the carboxylase Rubisco. The carboxysome self-assembles from thousands of individual proteins into icosahedral-like particles with a dense enzyme cargo encapsulated within a proteinaceous shell. In the case of the α-carboxysome, there is little molecular insight into protein-protein interactions that drive the assembly process. Here, studies on the α-carboxysome from Halothiobacillus neapolitanus demonstrate that Rubisco interacts with the N terminus of CsoS2, a multivalent, intrinsically disordered protein. X-ray structural analysis of the CsoS2 interaction motif bound to Rubisco reveals a series of conserved electrostatic interactions that are only made with properly assembled hexadecameric Rubisco. Although biophysical measurements indicate that this single interaction is weak, its implicit multivalency induces high-affinity binding through avidity. Taken together, our results indicate that CsoS2 acts as an interaction hub to condense Rubisco and enable efficient α-carboxysome formation.
- Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: