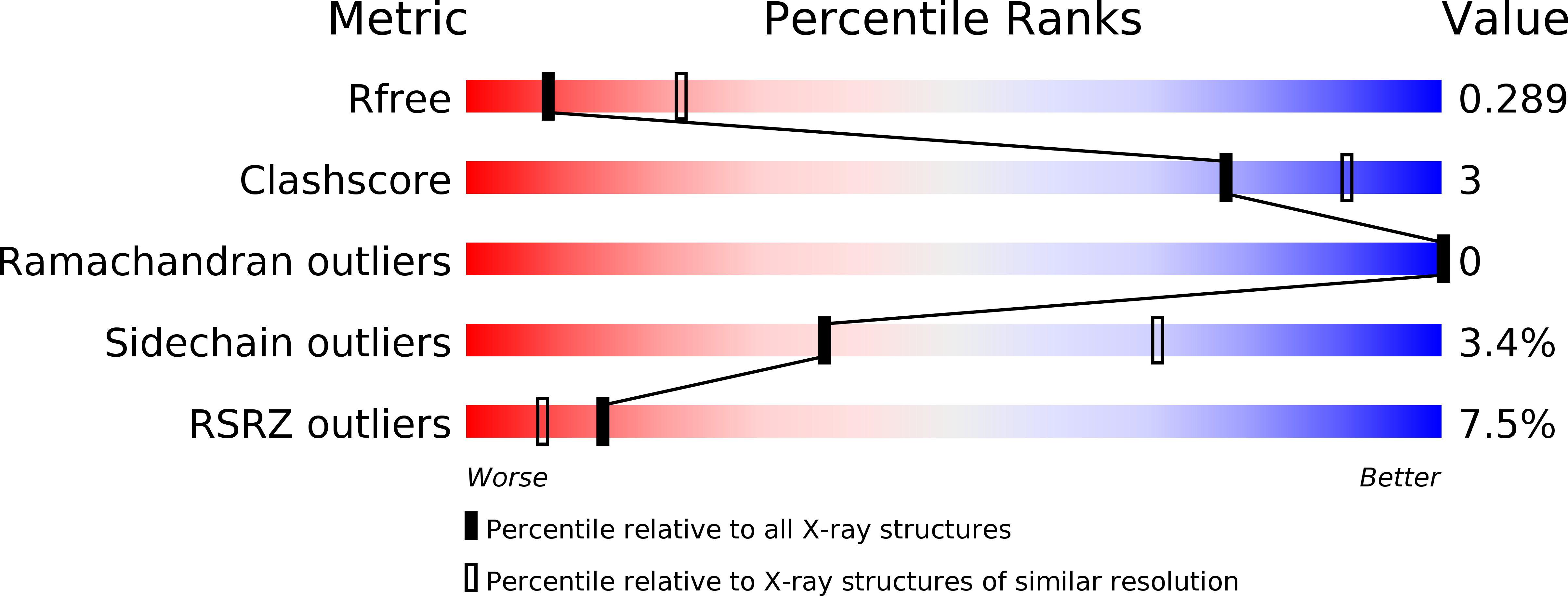
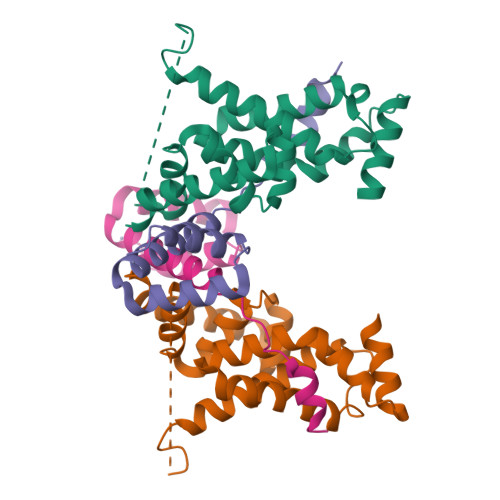
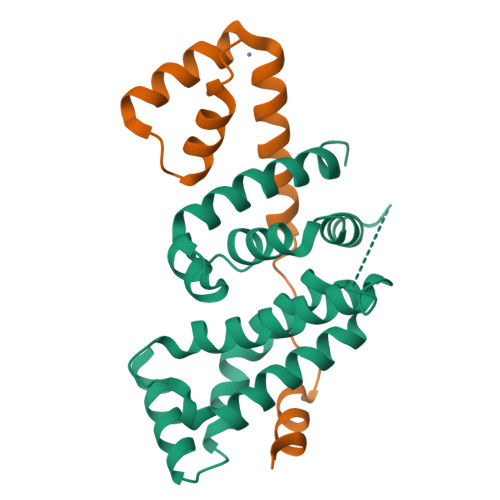
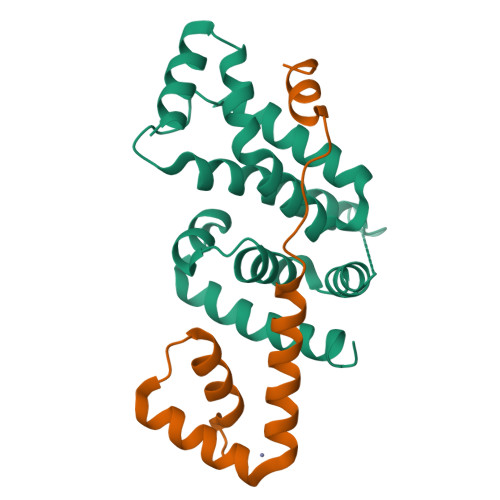
Structural insights into the regulation of Bacillus subtilis SigW activity by anti-sigma RsiW
Devkota, S.R., Kwon, E., Ha, S.C., Chang, H.W., Kim, D.Y.(2017) PLoS One 12: e0174284-e0174284
- PubMed: 28319136
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174284
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WUQ, 5WUR - PubMed Abstract:
Bacillus subtilis SigW is localized to the cell membrane and is inactivated by the tight interaction with anti-sigma RsiW under normal growth conditions. Whereas SigW is discharged from RsiW binding and thus initiates the transcription of its regulon under diverse stress conditions such as antibiotics and alkaline shock. The release and activation of SigW in response to extracytoplasmic signals is induced by the regulated intramembrane proteolysis of RsiW. As a ZAS (Zinc-containing anti-sigma) family protein, RsiW has a CHCC zinc binding motif, which implies that its anti-sigma activity may be regulated by the state of zinc coordination in addition to the proteolytic cleavage of RsiW. To understand the regulation mode of SigW activity by RsiW, we determined the crystal structures of SigW in complex with the cytoplasmic domain of RsiW, and compared the conformation of the CHCC motif in the reduced/zinc binding and the oxidized states. The structures revealed that RsiW inhibits the promoter binding of SigW by interacting with the surface groove of SigW. The interaction between SigW and RsiW is not disrupted by the oxidation of the CHCC motif in RsiW, suggesting that SigW activity might not be regulated by the zinc coordination states of the CHCC motif.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Pharmacy, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan, Gyeongbuk, South Korea.