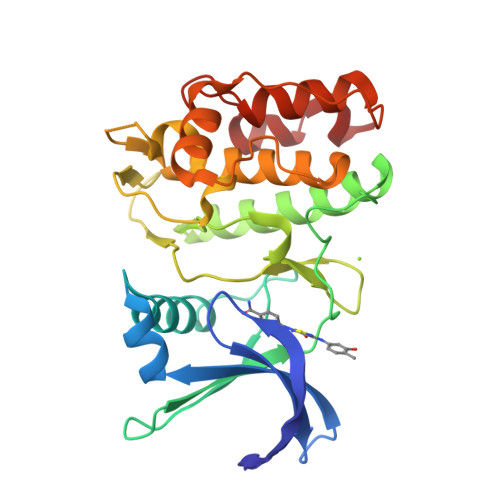
1,2,6-Thiadiazinones as Novel Narrow Spectrum Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Kinase 2 (CaMKK2) Inhibitors.
Asquith, C.R.M., Godoi, P.H., Counago, R.M., Laitinen, T., Scott, J.W., Langendorf, C.G., Oakhill, J.S., Drewry, D.H., Zuercher, W.J., Koutentis, P.A., Willson, T.M., Kalogirou, A.S.(2018) Molecules 23
- PubMed: 29783765
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051221
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VT1 - PubMed Abstract:
We demonstrate for the first time that 4 H -1,2,6-thiadiazin-4-one (TDZ) can function as a chemotype for the design of ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors. Using insights from a co-crystal structure of a 3,5-bis(arylamino)-4 H -1,2,6-thiadiazin-4-one bound to calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CaMKK2), several analogues were identified with micromolar activity through targeted displacement of bound water molecules in the active site. Since the TDZ analogues showed reduced promiscuity compared to their 2,4-dianilinopyrimidine counter parts, they represent starting points for development of highly selective kinase inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC 27599, USA. chris.asquith@unc.edu.