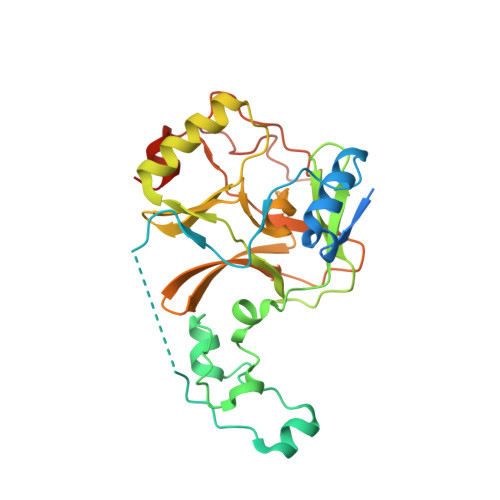
Molecular basis for the role of oncogenic histone mutations in modulating H3K36 methylation.
Zhang, Y., Shan, C.M., Wang, J., Bao, K., Tong, L., Jia, S.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 43906-43906
- PubMed: 28256625
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43906
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5V21, 5V22 - PubMed Abstract:
Histone H3 lysine 36 methylation (H3K36me) is critical for epigenetic regulation and mutations at or near H3K36 are associated with distinct types of cancers. H3K36M dominantly inhibits H3K36me on wild-type histones, whereas H3G34R/V selectively affects H3K36me on the same histone tail. Here we report the crystal structures of SETD2 SET domain in complex with an H3K36M peptide and SAM or SAH. There are large conformational changes in the substrate binding regions of the SET domain, and the K36M residue interacts with the catalytic pocket of SETD2. H3G34 is surrounded by a very narrow tunnel, which excludes larger amino acid side chains. H3P38 is in the trans configuration, and the cis configuration is incompatible with SETD2 binding. Finally, mutations of H3G34 or H3P38 alleviate the inhibitory effects of H3K36M on H3K36me, demonstrating that the stable interaction of H3K36M with SETD2 is critical for its inhibitory effects.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA.