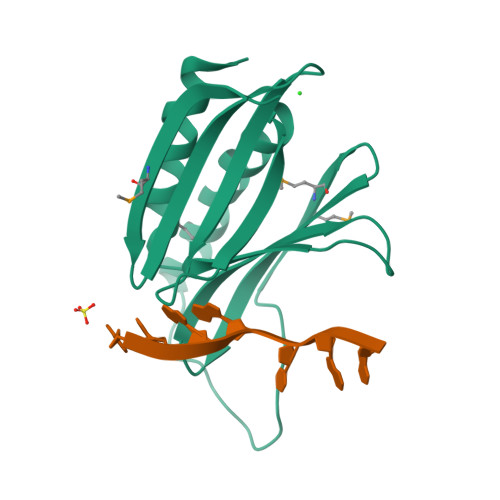
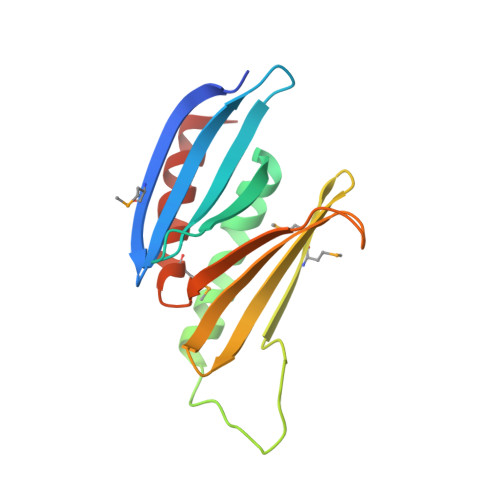
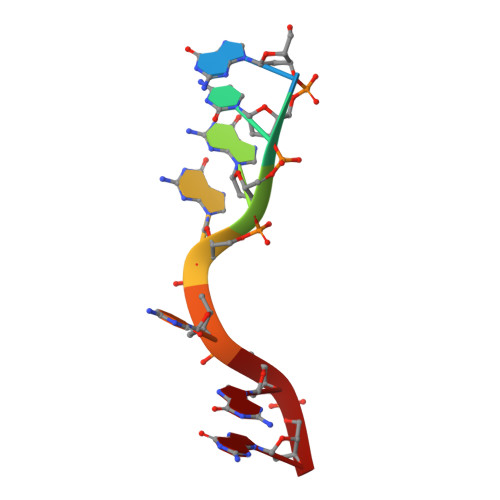
Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha.
Weber, J., Bao, H., Hartlmuller, C., Wang, Z., Windhager, A., Janowski, R., Madl, T., Jin, P., Niessing, D.(2016) Elife 5
- PubMed: 26744780
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5FGO, 5FGP - PubMed Abstract:
The neuronal DNA-/RNA-binding protein Pur-alpha is a transcription regulator and core factor for mRNA localization. Pur-alpha-deficient mice die after birth with pleiotropic neuronal defects. Here, we report the crystal structure of the DNA-/RNA-binding domain of Pur-alpha in complex with ssDNA. It reveals base-specific recognition and offers a molecular explanation for the effect of point mutations in the 5q31.3 microdeletion syndrome. Consistent with the crystal structure, biochemical and NMR data indicate that Pur-alpha binds DNA and RNA in the same way, suggesting binding modes for tri- and hexanucleotide-repeat RNAs in two neurodegenerative RNAopathies. Additionally, structure-based in vitro experiments resolved the molecular mechanism of Pur-alpha's unwindase activity. Complementing in vivo analyses in Drosophila demonstrated the importance of a highly conserved phenylalanine for Pur-alpha's unwinding and neuroprotective function. By uncovering the molecular mechanisms of nucleic-acid binding, this study contributes to understanding the cellular role of Pur-alpha and its implications in neurodegenerative diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Structural Biology, Helmholtz Zentrum München - German Research Center for Environmental Health, Neuherberg, Germany.