Metabolite Regulation of Nuclear Localization of Carbohydrate-response Element-binding Protein (ChREBP): ROLE OF AMP AS AN ALLOSTERIC INHIBITOR.
Sato, S., Jung, H., Nakagawa, T., Pawlosky, R., Takeshima, T., Lee, W.R., Sakiyama, H., Laxman, S., Wynn, R.M., Tu, B.P., MacMillan, J.B., De Brabander, J.K., Veech, R.L., Uyeda, K.(2016) J Biological Chem 291: 10515-10527
- PubMed: 26984404
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.708982
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5F74 - PubMed Abstract:
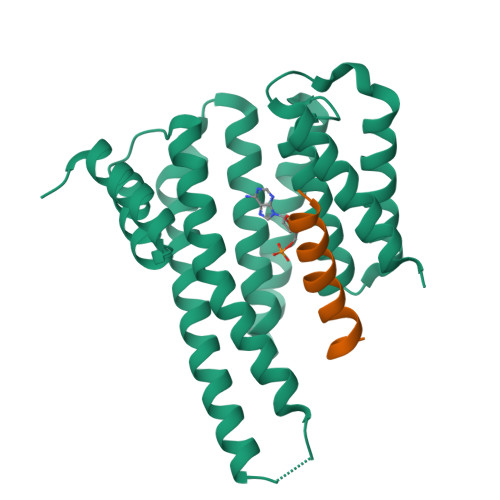
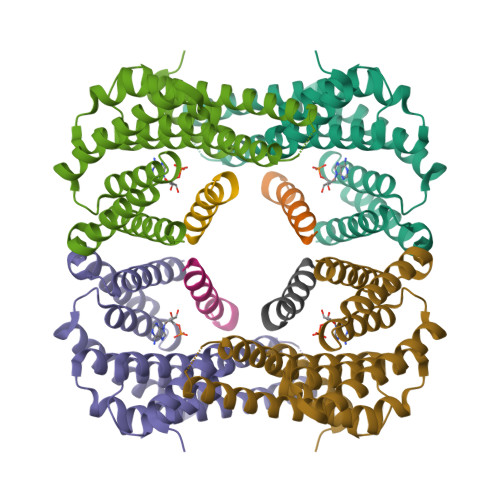
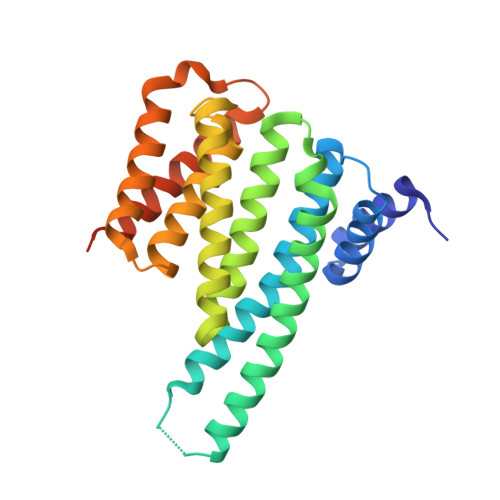
The carbohydrate-response element-binding protein (ChREBP) is a glucose-responsive transcription factor that plays an essential role in converting excess carbohydrate to fat storage in the liver. In response to glucose levels, ChREBP is regulated by nuclear/cytosol trafficking via interaction with 14-3-3 proteins, CRM-1 (exportin-1 or XPO-1), or importins. Nuclear localization of ChREBP was rapidly inhibited when incubated in branched-chain α-ketoacids, saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, or 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide. Here, we discovered that protein-free extracts of high fat-fed livers contained, in addition to ketone bodies, a new metabolite, identified as AMP, which specifically activates the interaction between ChREBP and 14-3-3. The crystal structure showed that AMP binds directly to the N terminus of ChREBP-α2 helix. Our results suggest that AMP inhibits the nuclear localization of ChREBP through an allosteric activation of ChREBP/14-3-3 interactions and not by activation of AMPK. AMP and ketone bodies together can therefore inhibit lipogenesis by restricting localization of ChREBP to the cytoplasm during periods of ketosis.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, Texas 75390.