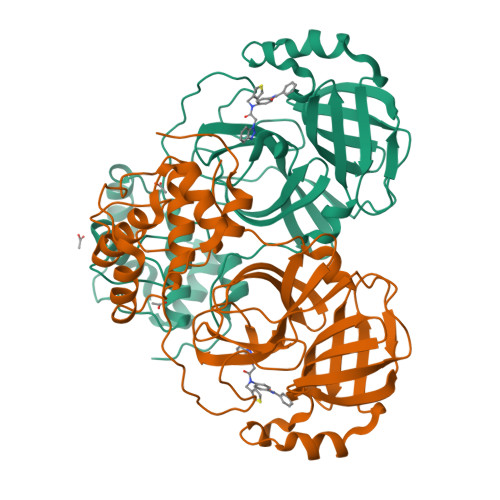
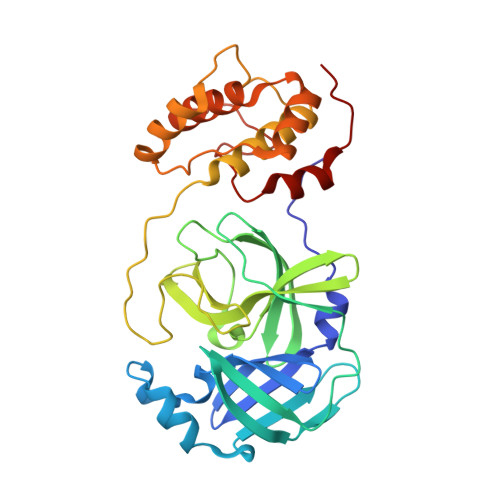
Targeting zoonotic viruses: Structure-based inhibition of the 3C-like protease from bat coronavirus HKU4-The likely reservoir host to the human coronavirus that causes Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS).
St John, S.E., Tomar, S., Stauffer, S.R., Mesecar, A.D.(2015) Bioorg Med Chem 23: 6036-6048
- PubMed: 26190463
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.06.039
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YO9, 4YOG, 4YOI, 4YOJ - PubMed Abstract:
The bat coronavirus HKU4 belongs to the same 2c lineage as that of the deadly Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and shows high sequence similarity, therefore potentiating a threat to the human population through a zoonotic shift or 'spill over' event. To date, there are no effective vaccines or antiviral treatments available that are capable of limiting the pathogenesis of any human coronaviral infection. An attractive target for the development of anti-coronaviral therapeutics is the 3C-like protease (3CL(pro)), which is essential for the progression of the coronaviral life cycle. Herein, we report the screening results of a small, 230-member peptidomimetic library against HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) and the identification of 43 peptidomimetic compounds showing good to excellent inhibitory potency of HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) with IC50 values ranging from low micromolar to sub-micromolar. We established structure-activity relationships (SARs) describing the important ligand-based features required for potent HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibition and identified a seemingly favored peptidic backbone for HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibition. To investigate this, a molecular sub-structural analysis of the most potent HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibitor was accomplished by the synthesis and testing of the lead peptidomimetic inhibitor's sub-structural components, confirming the activity of the favored backbone (22A) identified via SAR analysis. In order to elucidate the structural reasons for such potent HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibition by the peptidomimetics having the 22A backbone, we determined the X-ray structures of HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) in complex with three peptidomimetic inhibitors. Sequence alignment of HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro), and two other lineage C Betacoronaviruses 3CL(pro)'s, HKU5-CoV and MERS-CoV 3CL(pro), show that the active site residues of HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) that participate in inhibitor binding are conserved in HKU5-CoV and MERS-CoV 3CL(pro). Furthermore, we assayed our most potent HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibitor for inhibition of HKU5-CoV 3CL(pro) and found it to have sub-micromolar inhibitory activity (IC50=0.54±0.03μM). The X-ray structures and SAR analysis reveal critical insights into the structure and inhibition of HKU4-CoV 3CL(pro), providing fundamental knowledge that may be exploited in the development of anti-coronaviral therapeutics for coronaviruses emerging from zoonotic reservoirs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA; Department of Chemistry, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA; Centers for Cancer Research & Drug Discovery, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA.