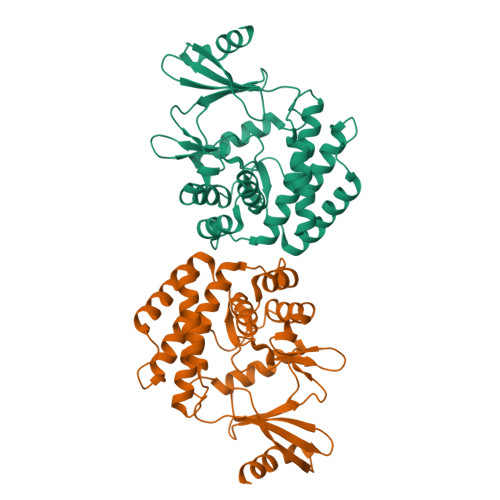
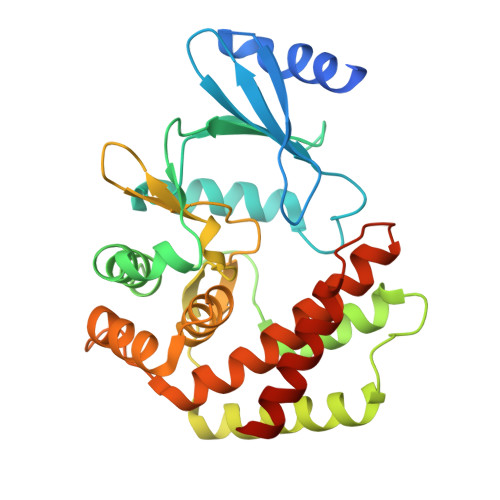
Structural and enzymatic characterization of the choline kinase LicA from Streptococcus pneumoniae
Wang, L., Jiang, Y.L., Zhang, J.R., Zhou, C.Z., Chen, Y.X.(2015) PLoS One 10: e0120467-e0120467
- PubMed: 25781969
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120467
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4R77, 4R78, 4R7B - PubMed Abstract:
LicA plays a key role in the cell-wall phosphorylcholine biosynthesis of Streptococcus pneumonia. Here we determined the crystal structures of apo-form LicA at 1.94 Å and two complex forms LicA-choline and LicA-AMP-MES, at 2.01 and 1.45 Å resolution, respectively. The overall structure adopts a canonical protein kinase-like fold, with the active site located in the crevice of the N- and C-terminal domains. The three structures present distinct poses of the active site, which undergoes an open-closed-open conformational change upon substrate binding and product release. The structure analyses combined with mutageneses and enzymatic assays enabled us to figure out the key residues for the choline kinase activity of LicA. In addition, structural comparison revealed the loop between helices α7 and α8 might modulate the substrate specificity and catalytic activity. These findings shed light on the structure and mechanism of the prokaryotic choline kinase LicA, and might direct the rational design of novel anti-pneumococcal drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026, People's Republic of China.