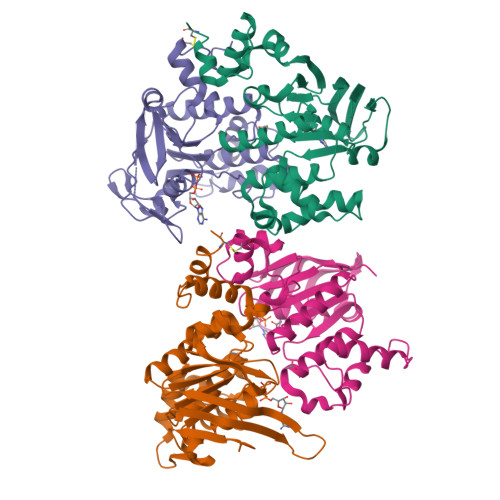
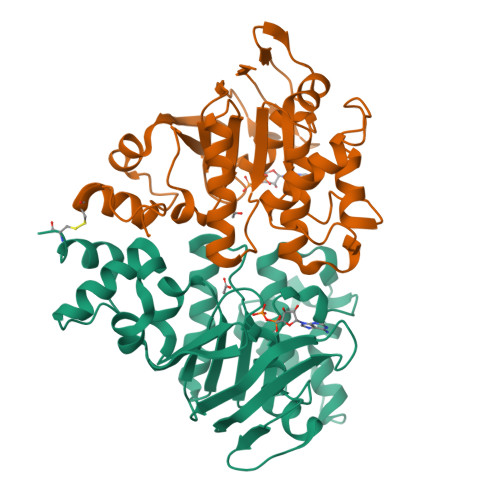
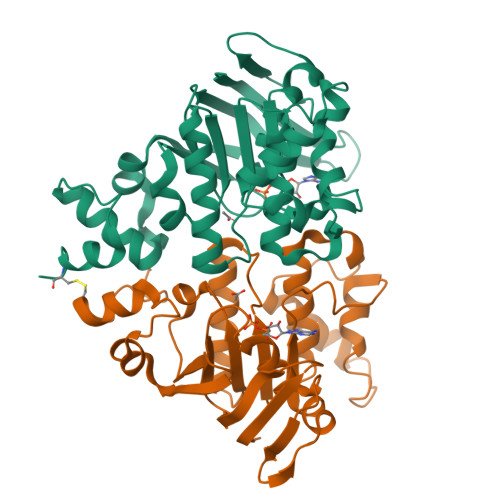
Assembly and mechanism of a group II ECF transporter.
Karpowich, N.K., Wang, D.N.(2013) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 2534-2539
- PubMed: 23359690
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217361110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
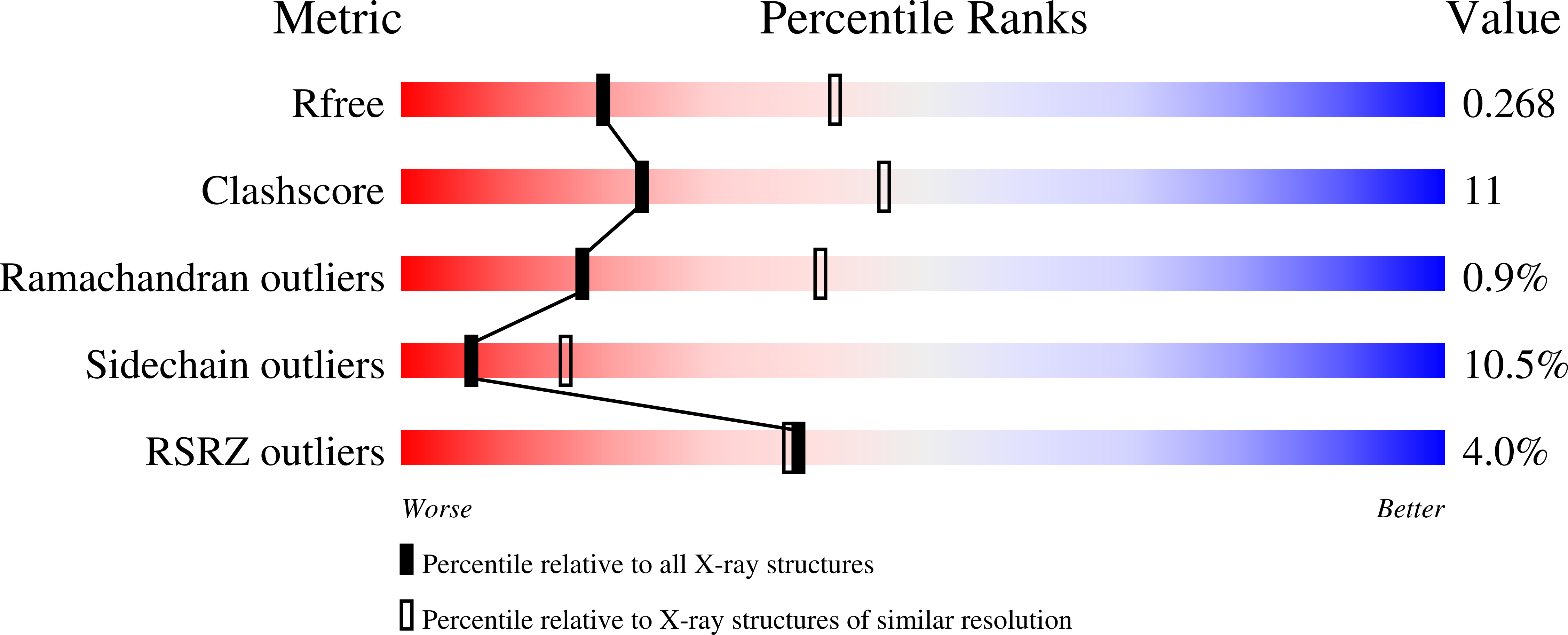
4HLU - PubMed Abstract:
Energy-coupling factor (ECF) transporters are a recently discovered family of primary active transporters for micronutrients and vitamins, such as biotin, thiamine, and riboflavin. Found exclusively in archaea and bacteria, including the human pathogens Listeria, Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus, ECF transporters may be the only means of vitamin acquisition in these organisms. The subunit composition of ECF transporters is similar to that of ATP binding cassette (ABC) importers, whereby both systems share two homologous ATPase subunits (A and A'), a high affinity substrate-binding subunit (S), and a transmembrane coupling subunit (T). However, the S subunit of ECF transporters is an integral membrane protein, and the transmembrane coupling subunits do not share an obvious sequence homology between the two transporter families. Moreover, the subunit stoichiometry of ECF transporters is controversial, and the detailed molecular interactions between subunits and the conformational changes during substrate translocation are unknown. We have characterized the ECF transporters from Thermotoga maritima and Streptococcus thermophilus. Our data suggests a subunit stoichiometry of 2S:2T:1A:1A' and that S subunits for different substrates can be incorporated into the same transporter complex simultaneously. In the first crystal structure of the A-A' heterodimer, each subunit contains a novel motif called the Q-helix that plays a key role in subunit coupling with the T subunits. Taken together, these findings suggest a mechanism for coupling ATP binding and hydrolysis to transmembrane transport by ECF transporters.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Helen L and Martin S Kimmel Center for Biology and Medicine, Skirball Institute of Biomolecular Medicine, and Department of Cell Biology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY 10016, USA. nathan.karpowich@med.nyu.edu