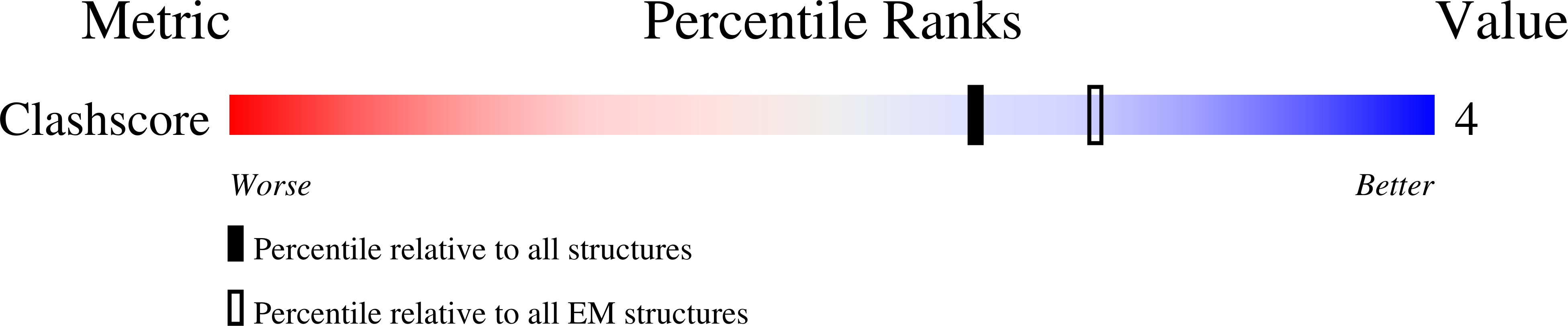Influence of the cytoplasmic domains of aquaporin-4 on water conduction and array formation.
Mitsuma, T., Tani, K., Hiroaki, Y., Kamegawa, A., Suzuki, H., Hibino, H., Kurachi, Y., Fujiyoshi, Y.(2010) J Mol Biol 402: 669-681
- PubMed: 20709083
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.07.060
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3IYZ - PubMed Abstract:
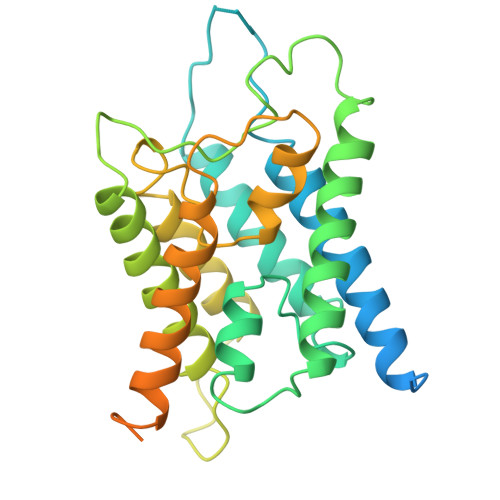
Phosphorylation of Ser180 in cytoplasmic loop D has been shown to reduce the water permeability of aquaporin (AQP) 4, the predominant water channel in the brain. However, when the structure of the S180D mutant (AQP4M23S180D), which was generated to mimic phosphorylated Ser180, was determined to 2.8 Å resolution using electron diffraction patterns, it showed no significant differences from the structure of the wild-type channel. High-resolution density maps usually do not resolve protein regions that are only partially ordered, but these can sometimes be seen in lower-resolution density maps calculated from electron micrographs. We therefore used images of two-dimensional crystals and determined the structure of AQP4M23S180D at 10 A resolution. The features of the 10-A density map are consistent with those of the previously determined atomic model; in particular, there were no indications of any obstruction near the cytoplasmic pore entrance. In addition, water conductance measurements, both in vitro and in vivo, show the same water permeability for wild-type and mutant AQP4M23, suggesting that the S180D mutation neither reduces water conduction through a conformational change nor reduces water conduction by interacting with a protein that would obstruct the cytoplasmic channel entrance. Finally, the 10-A map shows a cytoplasmic density in between four adjacent tetramers that most likely represents the association of four N termini. This finding supports the critical role of the N terminus of AQP4 in the stabilization of orthogonal arrays, as well as their interference through lipid modification of cysteine residues in the longer N-terminal isoform.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, Faculty of Science, Kyoto University, Oiwake, Kitashirakawa, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan.