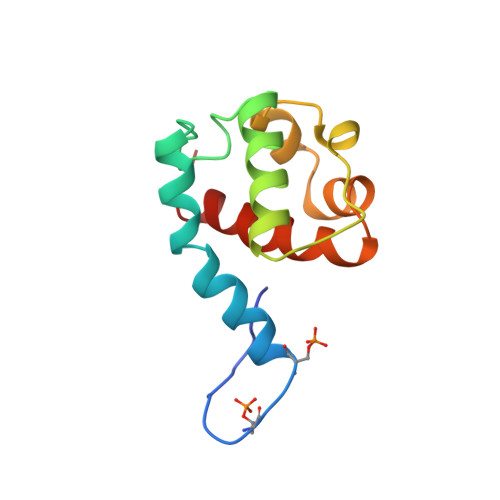
Ras signaling requires dynamic properties of Ets1 for phosphorylation-enhanced binding to coactivator CBP.
Nelson, M.L., Kang, H.S., Lee, G.M., Blaszczak, A.G., Lau, D.K., McIntosh, L.P., Graves, B.J.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 10026-10031
- PubMed: 20534573
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0915137107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
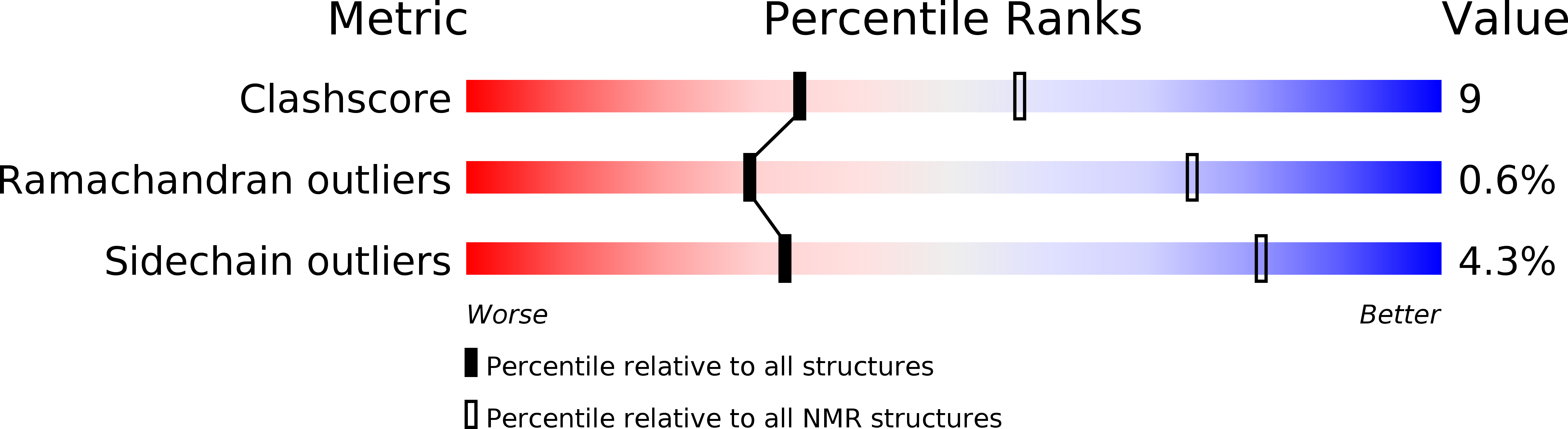
2KMD - PubMed Abstract:
Ras/MAPK signaling is often aberrantly activated in human cancers. The downstream effectors are transcription factors, including those encoded by the ETS gene family. Using cell-based assays and biophysical measurements, we have determined the mechanism by which Ras/MAPK signaling affects the function of Ets1 via phosphorylation of Thr38 and Ser41. These ERK2 phosphoacceptors lie within the unstructured N-terminal region of Ets1, immediately adjacent to the PNT domain. NMR spectroscopic analyses demonstrated that the PNT domain is a four-helix bundle (H2-H5), resembling the SAM domain, appended with two additional helices (H0-H1). Phosphorylation shifted a conformational equilibrium, displacing the dynamic helix H0 from the core bundle. The affinity of Ets1 for the TAZ1 (or CH1) domain of the coactivator CBP was enhanced 34-fold by phosphorylation, and this binding was sensitive to ionic strength. NMR-monitored titration experiments mapped the interaction surfaces of the TAZ1 domain and Ets1, the latter encompassing both the phosphoacceptors and PNT domain. Charge complementarity of these surfaces indicate that electrostatic forces act in concert with a conformational equilibrium to mediate phosphorylation effects. We conclude that the dynamic helical elements of Ets1, appended to a conserved structural core, constitute a phospho-switch that directs Ras/MAPK signaling to downstream changes in gene expression. This detailed structural and mechanistic information will guide strategies for targeting ETS proteins in human disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Oncological Sciences, University of Utah School of Medicine, Huntsman Cancer Institute, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, 84112, USA.