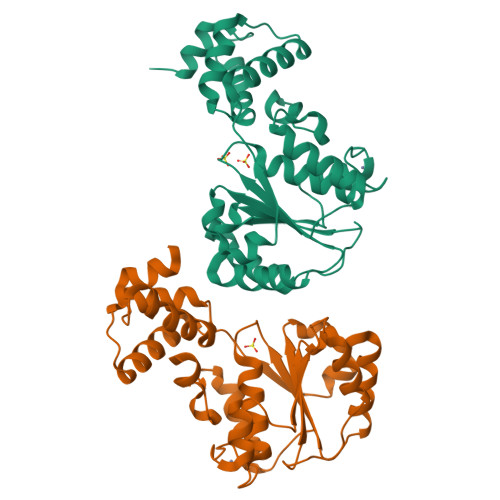
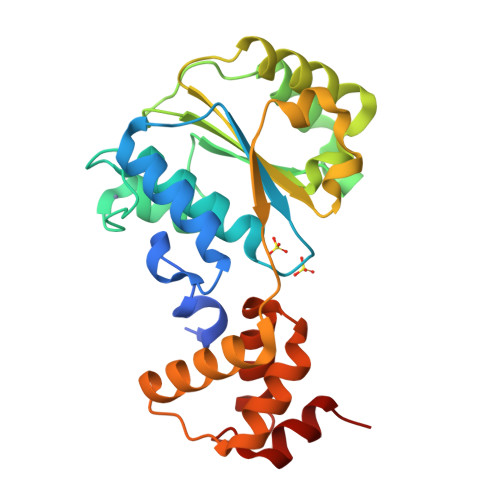
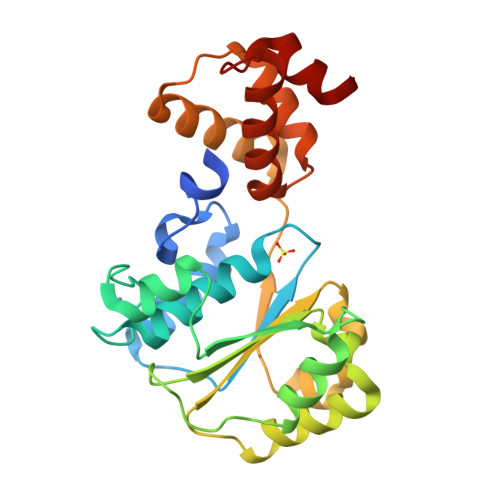
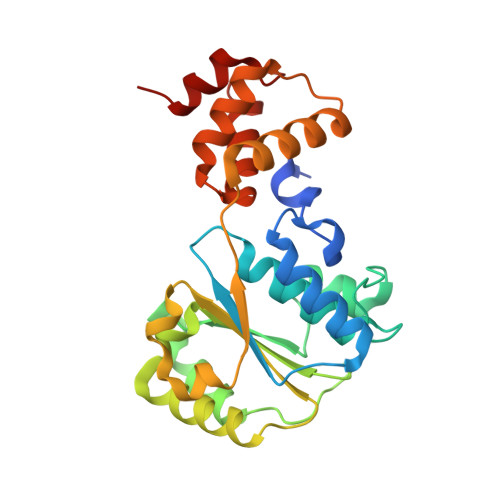
Nucleotide-Induced Conformational Changes in an Isolated Escherichia coli DNA Polymerase III Clamp Loader Subunit
Podobnik, M., Weitze, T.F., O'Donnell, M., Kuriyan, J.(2003) Structure 11: 253-263
- PubMed: 12623013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00027-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NJF, 1NJG - PubMed Abstract:
Sliding clamps are loaded onto DNA by ATP-driven clamp loader complexes. The structure of the E. coli clamp loader in a nucleotide-free state has been determined previously. We now report crystal structures of a truncated form of the isolated gamma-ATPase subunit, gamma(1-243), of the E. coli clamp loader, in nucleotide-free and bound forms. The gamma subunit adopts a defined conformation when empty, in which the nucleotide binding site is blocked. The binding of either ATPgammaS or ADP, which are shown to bind with equal affinity to gamma(1-243), induces a change in the relative orientation of the two domains such that nucleotides can be accommodated. This change would break one of the gamma:gamma interfaces seen in the empty clamp loader complex, and may represent one step in the activation process.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA.