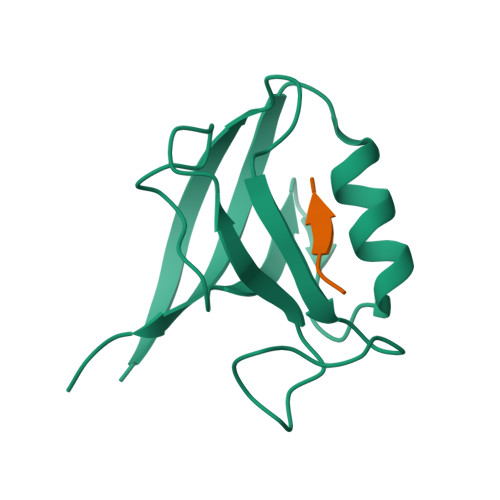
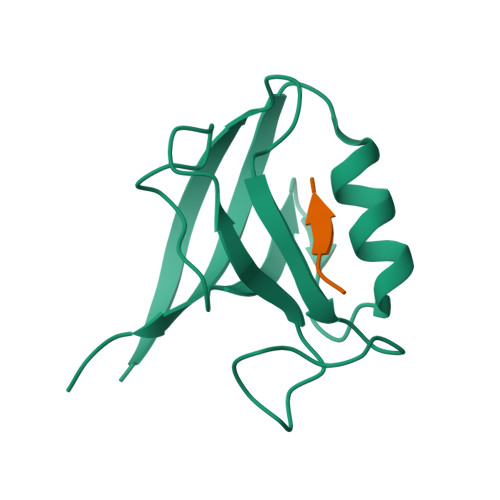
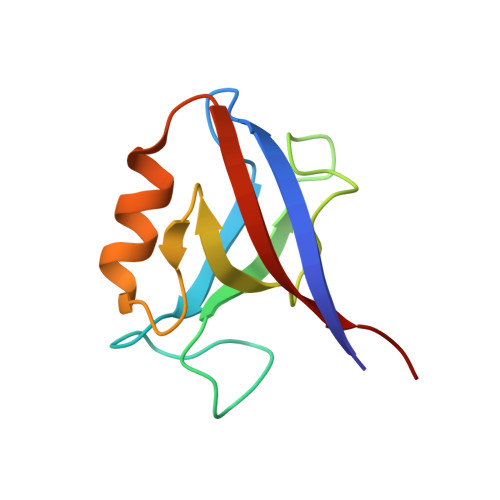
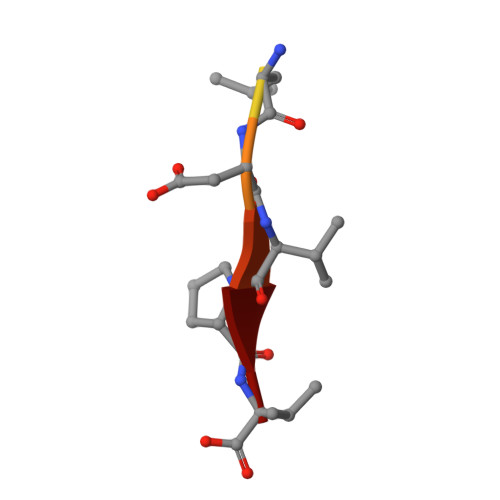
Novel mode of ligand recognition by the erbin PDZ domain
Birrane, G., Chung, J., Ladias, J.A.(2003) J Biological Chem 278: 1399-1402
- PubMed: 12444095
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C200571200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MFG, 1MFL - PubMed Abstract:
Erbin contains a class I PDZ domain that binds to the C-terminal region of the receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2, a class II ligand. The crystal structure of the human Erbin PDZ bound to the peptide EYLGLDVPV corresponding to the C-terminal residues 1247-1255 of human ErbB2 has been determined at 1.25-A resolution. The Erbin PDZ deviates from the canonical PDZ fold in that it contains a single alpha-helix. The isopropyl group of valine at position -2 of the ErbB2 peptide interacts with the Erbin Val(1351) and displaces the peptide backbone away from the alpha-helix, elucidating the molecular basis of class II ligand recognition by a class I PDZ domain. Strikingly, the phenolic ring of tyrosine -7 enters into a pocket formed by the extended beta 2-beta 3 loop of the Erbin PDZ. Phosphorylation of tyrosine -7 abolishes this interaction but does not affect the binding of the four C-terminal peptidic residues to PDZ, as revealed by the crystal structure of the Erbin PDZ complexed with a phosphotyrosine-containing ErbB2 peptide. Since phosphorylation of tyrosine -7 plays a critical role in ErbB2 function, the selective binding and sequestration of this residue in its unphosphorylated state by the Erbin PDZ provides a novel mechanism for regulation of the ErbB2-mediated signaling and oncogenicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Medicine Laboratory and Macromolecular Crystallography Unit, Division of Experimental Medicine, Harvard Institutes of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.