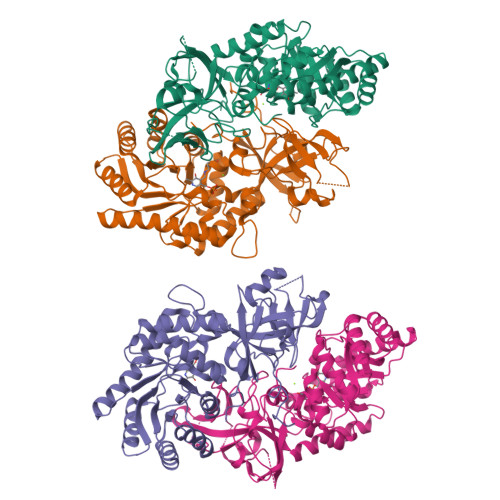
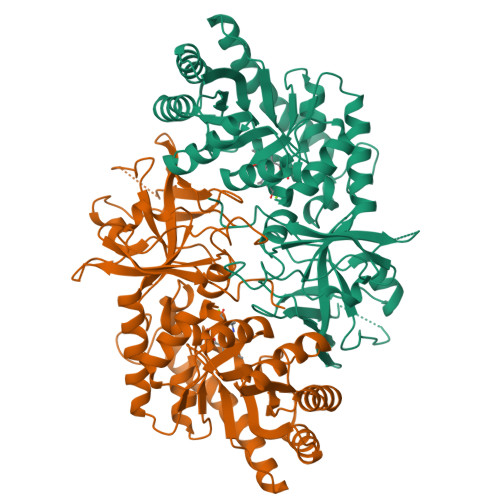
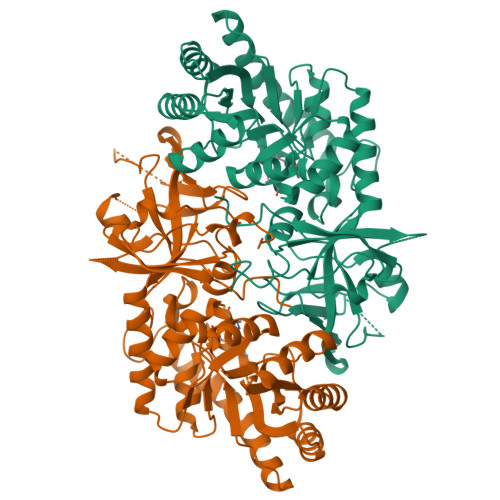
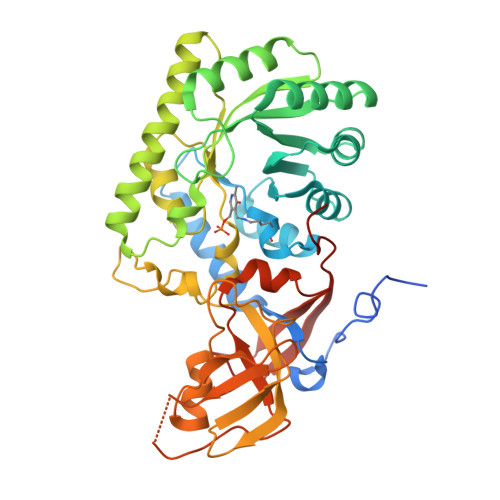
Structure of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-bound D-threonine aldolase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Hirato, Y., Goto, M., Mizobuchi, T., Muramatsu, H., Tanigawa, M., Nishimura, K.(2023) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 79: 31-37
- PubMed: 36748339
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X23000304
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YQA - PubMed Abstract:
D-Threonine aldolase (DTA) is a pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme which catalyzes the reversible aldol reaction of glycine with a corresponding aldehyde to yield the D-form β-hydroxy-α-amino acid. This study produced and investigated the crystal structure of DTA from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (CrDTA) at 1.85 Å resolution. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the crystal structure of eukaryotic DTA. Compared with the structure of bacterial DTA, CrDTA has a similar arrangement of active-site residues. On the other hand, we speculated that some non-conserved residues alter the affinity for substrates and inhibitors. The structure of CrDTA could provide insights into the structural framework for structure-guided protein engineering studies to modify reaction selectivity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Science, Faculty of Science, Toho University, 2-2-1 Miyama, Funabashi, Chiba 274-8510, Japan.