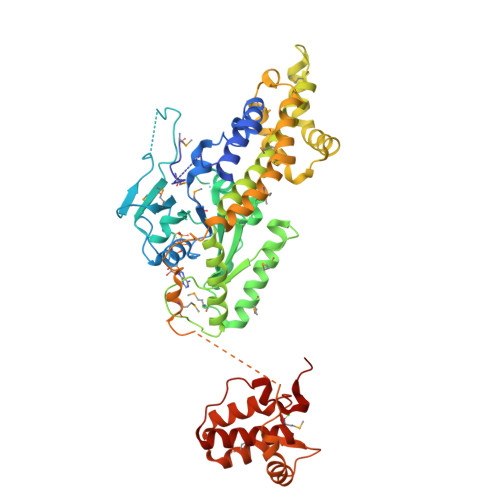
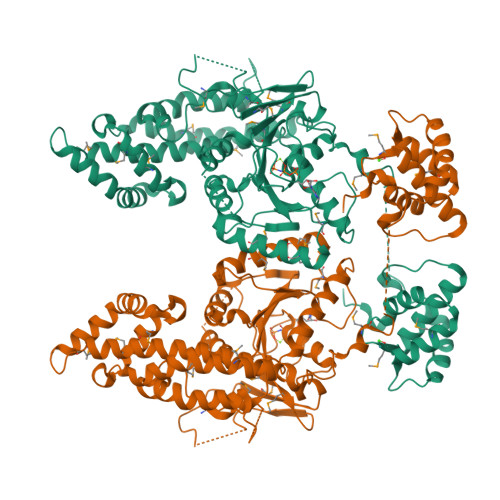
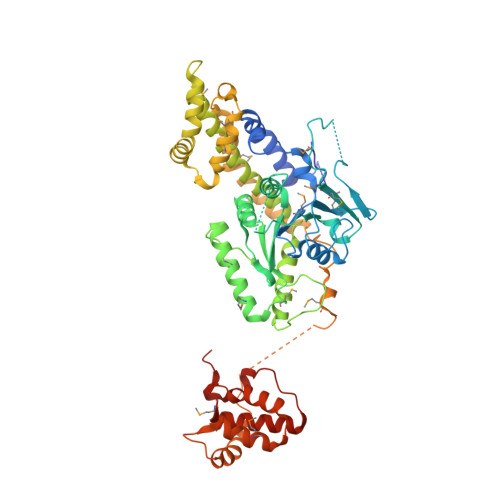
Structural Insights Into Membrane Interaction and Caveolar Targeting of Dynamin-Like Ehd2.
Shah, C., Hegde, B.G., Mor, B., Behrmann, E., Mielke, T., Moenke, G., Spahn, C.M., Lundmark, R., Daumke, O., Langen, R.(2014) Structure 22: 409
- PubMed: 24508342
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.12.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CID - PubMed Abstract:
The dynamin-related Eps15-homology domain-containing protein 2 (EHD2) is a membrane-remodeling ATPase that regulates the dynamics of caveolae. Here, we established an electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) approach to characterize structural features of membrane-bound EHD2. We show that residues at the tip of the helical domain can insert into the membrane and may create membrane curvature by a wedging mechanism. Using EPR and X-ray crystallography, we found that the N terminus is folded into a hydrophobic pocket of the GTPase domain in solution and can be released into the membrane. Cryoelectron microscopy demonstrated that the N terminus is not essential for oligomerization of EHD2 into a membrane-anchored scaffold. Instead, we found a function of the N terminus in regulating targeting and stable association of EHD2 to caveolae. Our data uncover an unexpected, membrane-induced regulatory switch in EHD2 and demonstrate the versatility of EPR to study structure and function of dynamin superfamily proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine, Crystallography, Robert-Rössle-Straße 10, 13092 Berlin, Germany.