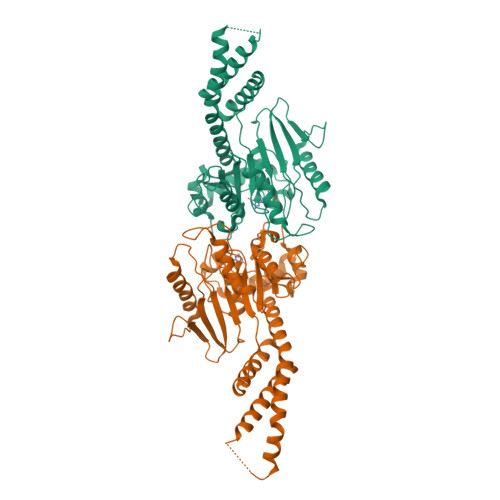
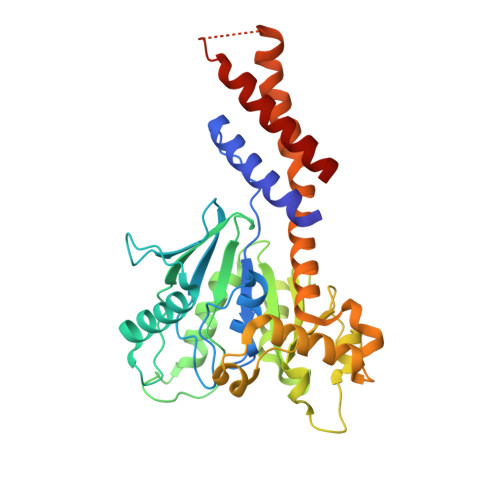
A Pseudoatomic Model of the Dynamin Polymer Identifies a Hydrolysis-Dependent Powerstroke.
Chappie, J.S., Mears, J.A., Fang, S., Leonard, M., Schmid, S.L., Milligan, R.A., Hinshaw, J.E., Dyda, F.(2011) Cell 147: 209
- PubMed: 21962517
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ZYC, 3ZYS - PubMed Abstract:
The GTPase dynamin catalyzes membrane fission by forming a collar around the necks of clathrin-coated pits, but the specific structural interactions and conformational changes that drive this process remain a mystery. We present the GMPPCP-bound structures of the truncated human dynamin 1 helical polymer at 12.2 Å and a fusion protein, GG, linking human dynamin 1's catalytic G domain to its GTPase effector domain (GED) at 2.2 Å. The structures reveal the position and connectivity of dynamin fragments in the assembled structure, showing that G domain dimers only form between tetramers in sequential rungs of the dynamin helix. Using chemical crosslinking, we demonstrate that dynamin tetramers are made of two dimers, in which the G domain of one molecule interacts in trans with the GED of another. Structural comparison of GG(GMPPCP) to the GG transition-state complex identifies a hydrolysis-dependent powerstroke that may play a role in membrane-remodeling events necessary for fission.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.