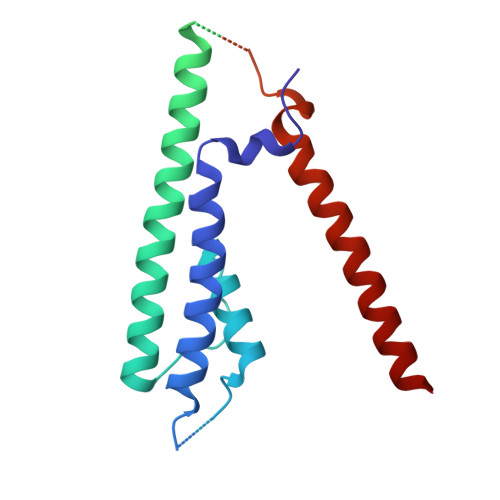
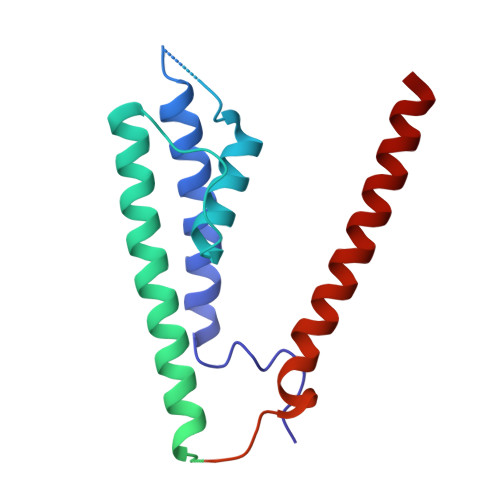
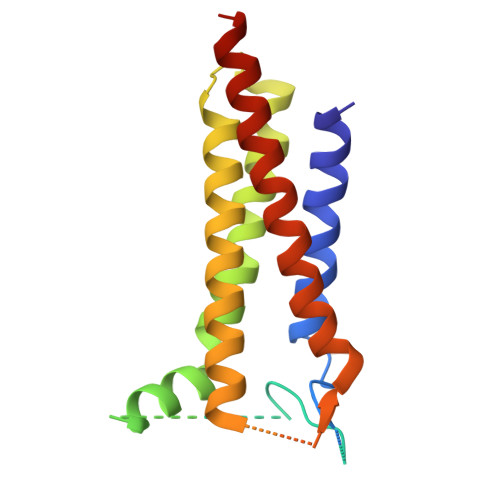
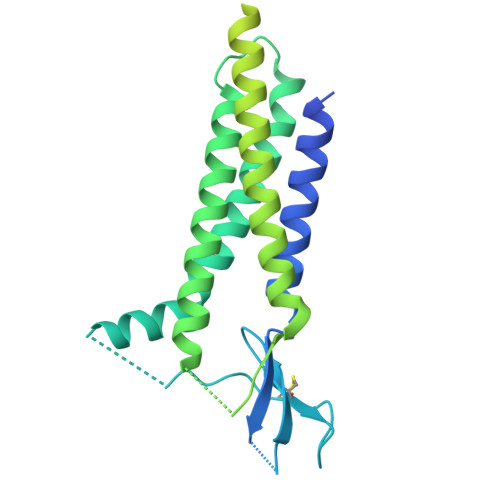
Efficient and rapid isolation of native AMPA receptor complexes for cryo-EM.
Park, J., Gouaux, E.(2026) Protein Sci 35: e70483-e70483
- PubMed: 41578975
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.70483
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9Z6U, 9Z6V, 9Z6W - PubMed Abstract:
Isolating native ion channels for structural characterization is routinely achieved by extraction from membrane fractions of tissue with prolonged mild detergent treatment. AMPA receptors (AMPARs), glutamatergic receptors that mediate fast excitatory transmission and synaptic plasticity, are coassembled with diverse auxiliary subunits and transiently-interacting partners to finely regulate processes from trafficking to gating kinetics. Previous studies of the composition and architecture of native AMPARs (nAMPARs) isolated from membrane fractions of rodent brain tissue have revealed many different subunit compositions and non-stochastic assemblies of the auxiliary subunits. However, elucidating the molecular architectures of nAMPARs complexed with less populated or transiently bound proteins has proven challenging. Here, we employ strategies for the rapid solubilization and purification of nAMPARs to increase the likelihood of isolating the greatest range of nAMPARs complexes. By utilizing whole brain tissue and reducing solubilization and purification duration, we purify nAMPARs complexed with a wider variety of auxiliary subunits and binding partners in a sufficient quantity and purity for cryo-electron microscopy studies. We resolve previously unreported subunit compositions and conformations that include ones with a half-splayed ATD layer, as well as complexes with four distinct auxiliary subunit arrangements in the TMD layer.
- Vollum Institute, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Oregon, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: