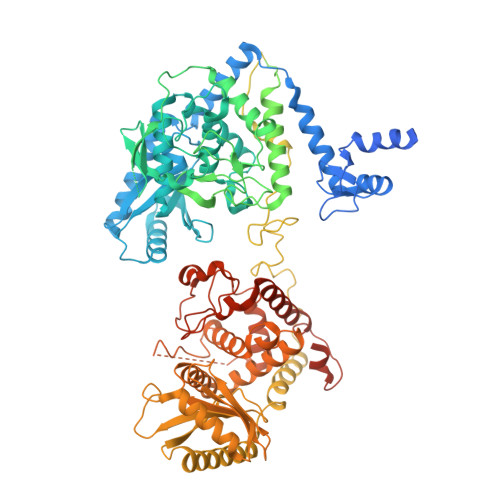
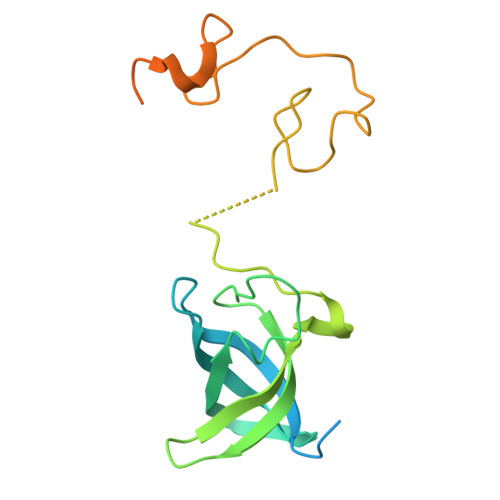
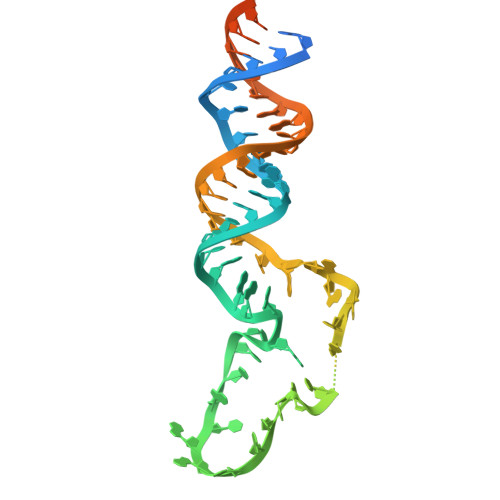
Mechanistic insights into Lin28-dependent oligo-uridylylation of pre-let-7 by TUT4.
Han, X., Yamashita, S., Tomita, K.(2026) Nucleic Acids Res 54
- PubMed: 41521656
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf1421
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9W4R, 9W4S - PubMed Abstract:
Lin28-dependent oligo-uridylylation of precursor let-7 (pre-let-7) by terminal uridylyltransferases 4 and 7 (TUT4/7) represses let-7 expression by blocking Dicer processing, thereby regulating cell differentiation and proliferation. The interaction between the Lin28:pre-let-7 complex and the N-terminal Lin28-interacting module (LIM) of TUT4/7 is required for pre-let-7 oligo-uridylylation by the C-terminal catalytic module (CM). Here, we report the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of human TUT4 complexed with Lin28A and oligo-uridylated pre-let-7, representing the elongation stage of oligo-uridylylation. Structural and biochemical analyses suggest that, after recruitment of pre-let-7 to the LIM through interactions between its terminal stem-loop and Lin28A, the CM associates with the LIM through protein-protein interactions. The double-stranded stem region of pre-let-7 is surrounded by the CM and LIM, the upper portion of the duplex unwinds, and the 3' end of pre-let-7 is positioned in the CM catalytic site for the initiation of oligo-uridylylation. At the oligo-uridylylation stage, the CM finger domain clamps the double-stranded region of pre-let-7, thereby further stabilizing the pre-let-7:TUT4 complex, enabling processive elongation of the uridine tail by the CM. Thus, the LIM functions as a stable anchor, working together with Lin28A to ensure efficient and processive oligo-uridylylation of pre-let-7.
- Department of Computational Biology and Medical Sciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8562, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: