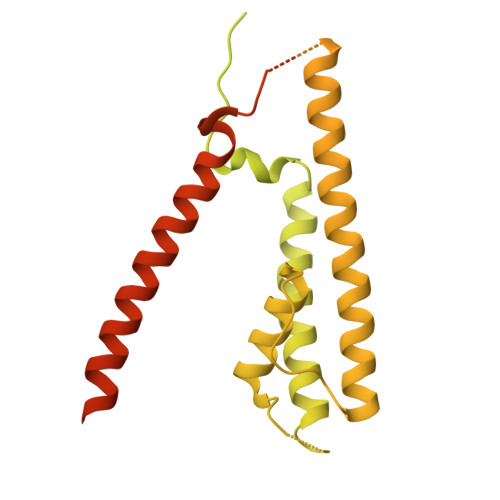
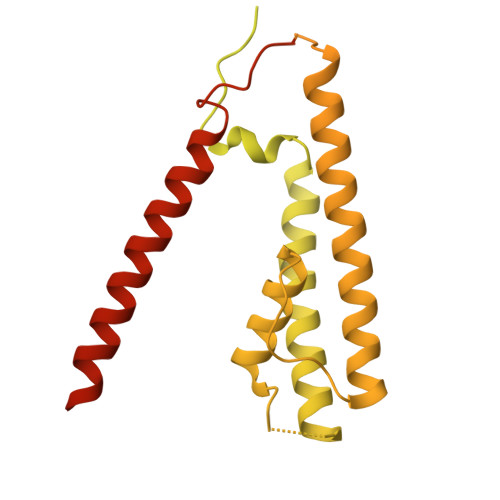
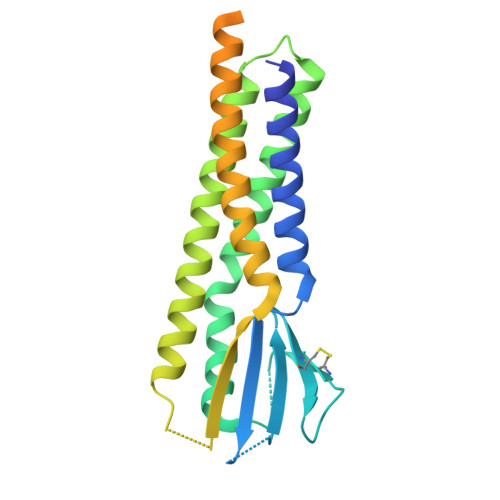
Structure and organization of AMPA receptor-TARP complexes in the mammalian cerebellum.
Scrutton, A.M., Sengupta, N., Ivica, J., Stockwell, I., Peak-Chew, S., Singh, B., Suzuki, K., Chang, V.T., McLaughlin, S.H., Krieger, J.M., Aricescu, A.R., Greger, I.H.(2025) Science : eaeb3577-eaeb3577
- PubMed: 41379938
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aeb3577
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9S3O, 9S3Q, 9S3Z, 9S41 - PubMed Abstract:
AMPA receptors (AMPARs) are multimodal transducers of glutamatergic signals throughout the brain. Their diversity is exemplified in the cerebellum; at afferent synapses, AMPARs mediate high-frequency excitation, whereas in Bergmann glia (BG) they support calcium transients that modulate synaptic transmission. This spectrum arises from different combinations of core subunits (GluA1-4), auxiliary proteins, and post-transcriptional modifications. Here, using mass-spectrometry, cryo-EM, and electrophysiology, we characterize major cerebellar AMPARs in pig: calcium-impermeable GluA2/A4 heteromers with four TARP subunits, mainly neuronal in origin, and BG-specific calcium-permeable GluA1/A4 heteromers containing two Type-2 TARPs. We also showed that GluA4 receptors consistently exhibit compact N-terminal domains that promote their synaptic delivery. Our study defines the organizational principles of mammalian cerebellar AMPAR complexes and reveals how different receptor subtypes support cell-type specific functions.
- Neurobiology Division, Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: