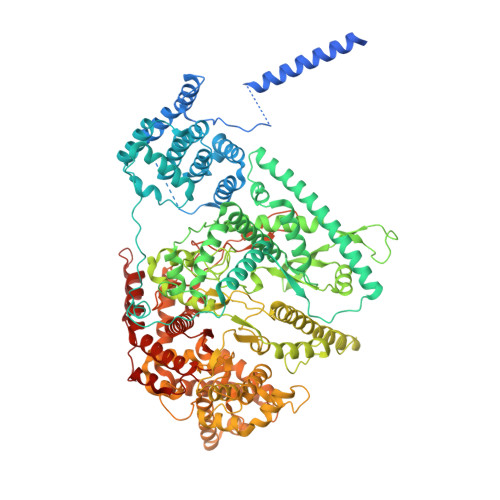
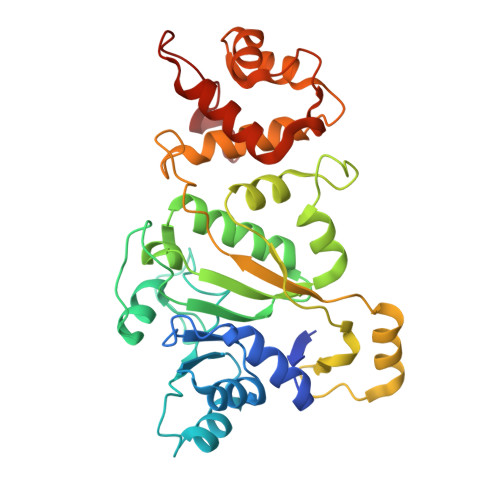
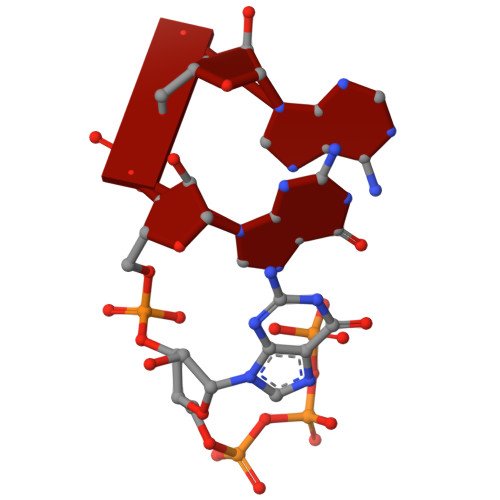
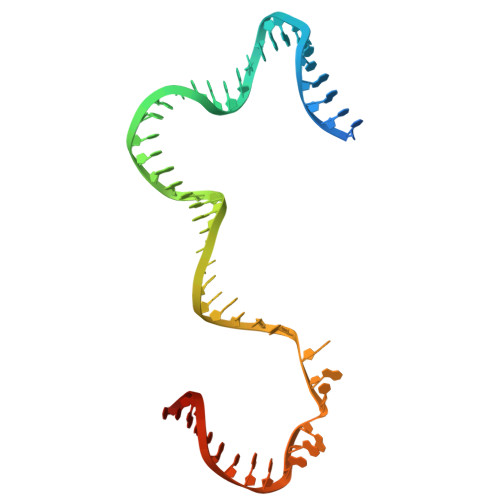
Human mitochondrial RNA polymerase structures reveal transcription start site and slippage mechanism.
Shen, J., Goovaerts, Q., Ajjugal, Y., De Wijngaert, B., Das, K., Patel, S.S.(2025) Mol Cell 85: 3137-3150.e7
- PubMed: 40712586
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2025.07.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9GZM, 9GZN, 9GZO, 9R95, 9R96 - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription of the human mitochondrial DNA is initiated by POLRMT and initiation factors mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) and mitochondrial transcription factor B2 (TFB2M). We present cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of three transcription initiation intermediates (pre-catalytic IC3 [pre-IC3], slipped-IC3, and slipped pre-IC4) catalyzing RNA synthesis by normal and slippage pathways with fully resolved transcription bubbles and RNA transcripts starting from the +1 or -1 position. The structural and biochemical studies reveal mechanisms of promoter melting, start site selection, and slippage synthesis. Promoter melting begins at -4 with base-specific interactions of template -4 and -3 guanines with POLRMT and non-template -1 adenine with TFB2M. The NT-stabilizing loop (K 153 LDPRSGGVIKPP 165 ) and Y209 of TFB2M and W1026 of POLRMT interact with the non-template strand to guide initiation from the +1 start site. The -1 position is not an alternative start site but supports slippage initiation by base-pairing with a slipped or rebound 2-nt RNA. Cryo-EM resolved additional apo and dimeric complexes whose populations may regulate transcription initiation.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA; Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School of Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: