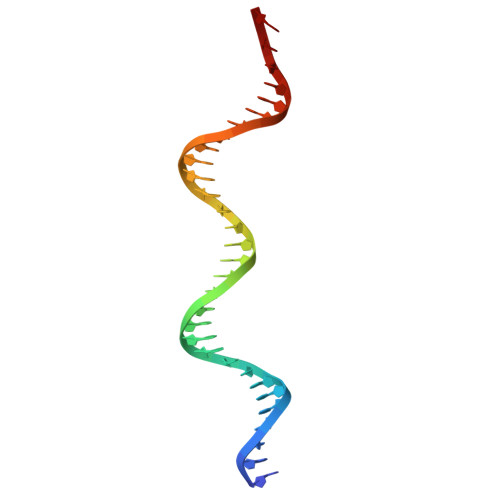
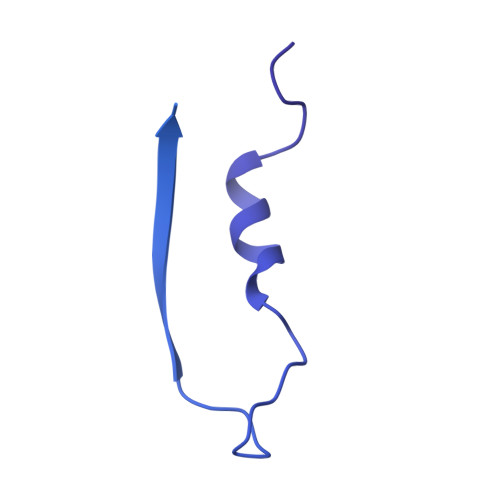
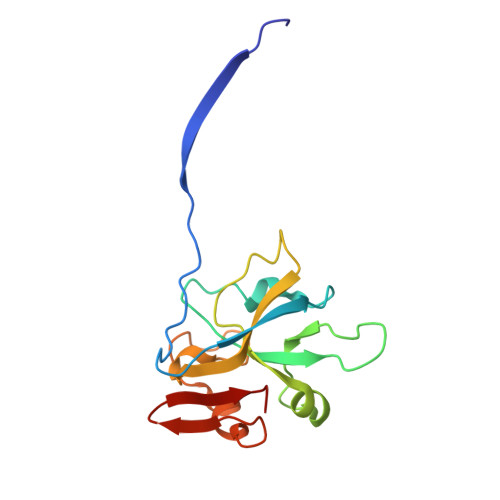
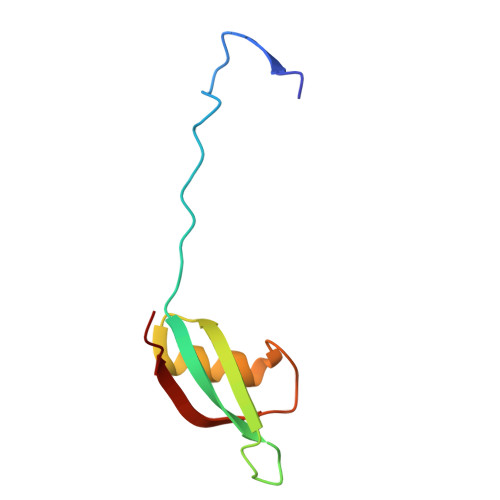
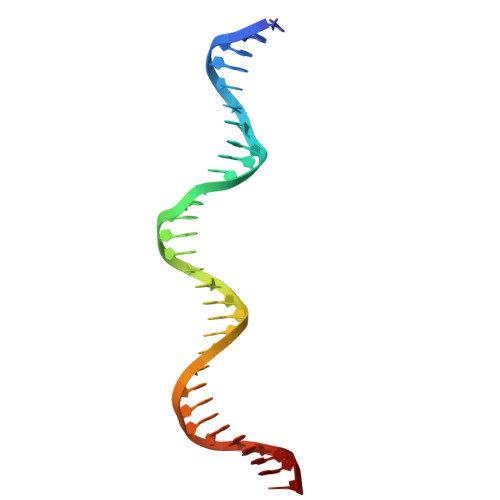
The structure of a thermostable phage's portal vertex and neck complex illuminates the headful maturation mechanism.
Sedivy, E.L., Agnello, E., Hobaugh, J.E., Ahsan, R., Song, K., Xu, C., Kelch, B.A.(2026) J Mol Biology : 169641-169641
- PubMed: 41544933
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2026.169641
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9OAB, 9OAC, 9OAD, 9OAE, 9Q7A - PubMed Abstract:
Viruses assemble from component parts inside their host cells, but the mechanisms coordinating this complex process are not completely understood. In tailed bacteriophages, the genome is packaged into its capsid shell through the portal complex. The portal complex then closes to retain DNA and connects to the tail, which is required for host recognition and infection. The trigger to stop pumping DNA and assemble the mature virus has been a longstanding conundrum in the field. We determined the structure of the portal, the proteins that connect it to the tail, and portal vertex in the hyperthermophilic phage Oshimavirus using cryo-Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM). We find highly intertwined loop structures, like in a wicker basket, potentially stabilizing the portal vertex against high temperatures. Moreover, we observe that the portal protrudes from the capsid in mature virions. We propose that portal is repositioned by packaged DNA, forming a pressure-sensitive switch that terminates genome packaging and triggers tail attachment in headful phages.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biotechnology, University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, Worcester MA.
Organizational Affiliation: