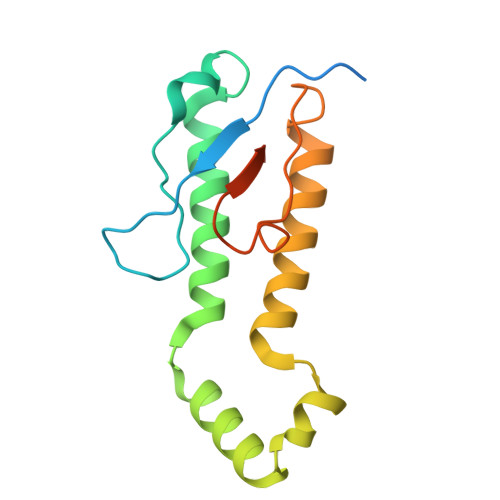
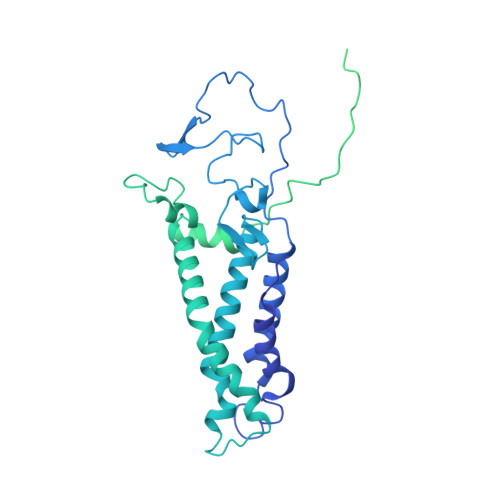
Functional dissection of the zDHHC palmitoyltransferase 5-golgin A7 palmitoylation complex.
Kahlson, M.A., Ritho, J., Gomes, J.V., Wang, H., Butterwick, J.A., Dixon, S.J.(2025) J Biological Chem 301: 110694-110694
- PubMed: 40930250
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110694
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9OA6 - PubMed Abstract:
Small molecules serve as valuable tools for probing nonapoptotic cell death mechanisms. The small molecule caspase independent lethal 56 (CIL56) induces a unique form of nonapoptotic cancer cell death that is promoted by a complex formed between zDHHC palmitoyltransferase 5 (ZDHHC5) and an accessory protein, golgin A7 (GOLGA7, also known as GCP16). The structure and function of this complex in nonapoptotic cell death regulation remain poorly understood. Here, we use coimmunoprecipitation, functional assays, and cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to elucidate the structure and function of the Zdhhc5-GOLGA7 complex. We identify key residues in both Zdhhc5 and GOLGA7 that are necessary for complex formation and to promote nonapoptotic cancer cell death in response to caspase independent lethal 56. These results provide new insights into the structure and function of a death-promoting protein complex.
- Department of Biology, Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: